Obstructive bronchitis is called severe inflammation of the bronchi, which is accompanied by obstruction. In other words, as a result of the inflammatory process, the lights of the bronchus taps, and a plentiful amount of mucus cannot fully retreat. This leads to sharp respiratory failure and vast swelling of the bronchi. This is the most dangerous form of bronchitis, which most often affects the kids who have crossed the three -year threshold. Although among adults this diagnosis is also found. What is the danger of this disease and how to recognize it in order to start treatment in time?
Content
- Form and degree of damage to obstructive bronchitis
- The reasons for obstructive bronchitis
- Obstructive bronchitis - symptoms
- Methods for diagnosing obstructive bronchitis
- Obstructive bronchitis - treatment
- Obstructive bronchitis - folk treatment
- Video "Obstructive bronchitis in children - Komarovsky"
Form and degree of damage to obstructive bronchitis
Obstructive bronchitis (from lat. Obstation means “obstruction”) - damage to the bronchial tree as a result of activating the inflammatory process. Pathology is manifested by an unproductive cough with sputum and severe shortness of breath.
More often the kids suffer from this disease. Its active and most severe variety is acute obstructive bronchitis. As a rule, such a diagnosis is made with prolonged wet coughing. Successful treatment allows you to completely defeat the disease, and it does not return anymore.
If therapy is ineffective, the pathology goes into a chronic form and often exacerbates. This condition is characteristic of the adult half of humanity and proceeds with its own characteristics. So, chronic obstructive bronchitis is characterized by a more global damage to the respiratory system:
- In 90% of cases, deep damage to the alveolar tissue is recorded.
- Bronkes -constructive (asthmatic) syndrome is formed, which can have both reversible and stable modifications of the respiratory tract.
- Secondary diffuse emphysema develops (the alveoli stretch, losing the ability to contract).
- Hypoxia of blood, tissues begins as a result of inferior ventilation of the lungs.
Depending on the cause of bronchitis, it can be contagious, for example, if it was provoked by a viral infection, or non -non -controversial (asthmatic or allergic obstructive bronchitis).
Important! Obstructive bronchitis is more often fixed among the population living in a wet climate with an average annual temperature of not higher than +17 ° C. Such conditions create favorable conditions for the development of fungi and viruses that cause recurrent obstructive bronchitis.
How does obstructive bronchitis develop? The development mechanism is simple: first, under the influence of an unfavorable factor, the cells of the ciliary epithelium are dying. Next, a pathological change in the density and composition of the mucus occurs. The secreted secret after a change in its composition loses the entire bactericidal barrier (the production of interferon and lactoerrin stops), leaving the bronchi without protection against pathogenic flora. The “surviving” number of cilia does not cope with the flow of sputum and completely slows down its movement. As a result, there is a stagnation of mucus (mucostasis).
The severity of the development of pathology is estimated by specific criteria and there are three degrees. The main indicator that allows you to evaluate the condition of the patient - OFV1. It denotes the volume of a strong exhalation that is done in a second. After receiving this indicator, one of the three stages of the disease is determined:
- Stage I: the OFV1 indicator exceeds 50% of the generally accepted norm. This is chronic obstructive bronchitis and treatment is not prescribed. The chronic course of the disease does not create any discomfort to the patient. The risk of developing irreversible disorders is minimal, but the patient should be registered with the doctor.
- Stage II: OFV1 borderline reduced to 34–49%. The disease greatly worsens the patient's well -being, so there is a gentle treatment and a systematic examination by a pulmonologist.
- Stage III: The OFV1 level is less than 34%. The symptomatic picture is bright, the quality of life is very lowered. The patient goes to the hospital for treatment, in some cases, outpatient treatment is permissible.
Depending on the course of the disease and the protective properties of the body, both reversible and irreversible modifications of the bronchus can occur.
The reversible changes include:
- bronchospasm;
- vast edema of the bronchi;
- crossing the mucus of the lumen of the bronchi.
Irreversible changes:
- narrowing of bronchial lumen;
- modification of bronchial tissues;
- emphysema and subsequent violation of air circulation in small bronchi.

The reasons for obstructive bronchitis
The disease, regardless of age, in most cases develops after the introduction of pathogenic microorganisms into the body - viruses, fungi, chlamydia, and coccal flora. But not always the penetrated infection is activated. In order for a person to get obstructive bronchitis, favorable conditions are needed.
Recently, cases of development of obstructive bronchitis have become more frequent after a long effect on the body of one of the following factors:
- Poor performance of the immune system.
- Spear or irrational nutrition.
- Poor absorption of food due to dysbiosis or chronic diseases of internal organs.
- Often repeated respiratory diseases (more than three times a year).
- The state of chronic stress.
An allergic predisposition in humans plays a special role in the formation of obstructive bronchitis. If the baby is prone to any allergic manifestations from an early age, then the risk in adulthood to obtain obstructive bronchitis of the chronic form increases very much. And the following reasons can contribute to this:
- smoking for many years;
- work with harmful conditions (miners, metallurgists, chemical workers);
- accommodation in an unfavorable zone (residents of large megacities);
- disruption of the respiratory tract toxic substances.
It is also worth emphasizing the role of internal provocateurs of the disease. Its formation is influenced by the II blood type, the genetically formed lack of immunoglobulin A, and the enzyme deficiency of alpha1-antitripsin.
In babies and adolescents, in addition to the aforementioned causes of the development of the disease, there are several more specific factors. So, the children belong to the risk group:
- With diagnosed rickets.
- With a low weight in the perinatal period.
- With poor indicators on the Apgar scale after birth.
- With diathesis, neurodermatitis or other allergic disease.
- Children who often had viral diseases until 1 year old.
- The babies that grew up on artificial feeding.
- Passive smoking (parents smoke at home).

Obstructive bronchitis - symptoms
Signs of the disease depend on age, the work of the immune system, as well as on the individual characteristics of the body. In addition, obstructive bronchitis manifests itself differently in the active phase and in a chronic course.
How obstructive bronchitis in children is manifested
Inflammation of the bronchi in babies is difficult. The acute form of obstructive bronchitis in childhood often develops due to the accession of viruses, for example, cytomegalovirus or adenovirus.
In children, the disease is especially difficult, with a clear deterioration in the state of health against the background of bright features. In the child, the symptoms of ordinary SARS come to the fore: he is capricious, heat appears, rhinitis, insignificant cough joins. Then the symptoms become more specific:
- the heat continues to hold on, it is difficult to knock down with antipyretic drugs;
- the cough intensifies, accompanied by bouts of difficulty breathing;
- sputum is absent or acquires a yellow-green tint;
- strengthening cough occurs in the morning immediately after awakening;
- in the baby, hesitations, similar to a whistle, are noticeable, shortness of breath is noted;
- the breath is very quicked, while the breath lengthens, and the exhalation is shortened;
- the throat is inflamed, blushes, tingling is felt;
- disturb the attacks of headaches, increasing sweating;
- during breathing, the child tries to swallow the air, involving several elements into the process: an intercostal zone, a jugular fossa, nasal wings;
- refusal of food, strong anxiety, crying, drowsiness may increase.
Important! The symptomatic picture of obstructive bronchitis and bronchiolite is very similar, therefore, a competent diagnosis is required for successful treatment, which allows you to distinguish one disease from another.
If the child is made an incorrect diagnosis and the inappropriate treatment is prescribed, the disease goes into a severe stage with the following signs:
- The child is not able to take a calm and deep breath.
- The skin acquires a bluish tint.
- The fever is rapidly increasing.
- Broncholytics cannot completely remove severe shortness of breath.
- A child can fully inhale only standing or sitting.
- If you lay the baby, his breathing becomes like a bubbling sound.
- Headaches become unbearable, dizziness, loss of consciousness may appear.

Signs of obstructive bronchitis in adults
In adults, an acute form of the disease rarely develops, but its symptoms will be the same as in children. But, the intensity of the symptoms is less pronounced, and does not increase so quickly.
Typically, in adulthood, a chronic form of the disease is already diagnosed. The patient can only have a slight shortness of breath, the release of mucus and cough with obstructive bronchitis.
After SARS, inflammation can become aggravated. This can be seen by such signs:
- Sputum changes color and density: it becomes thick, with an admixture of pus or a vein of blood.
- The cough is frequent, exhausting, with a characteristic whistle.
- Shortness is intensified, with severe inflammation of the bronchi, it is difficult for the patient to move quickly.
- From a lack of oxygen due to difficult inhalation on the face, cyanosis is noted (the nasolabial triangle is painted blue).
- Blood pressure rises, headache appears, aches in the muscles.
- Attacks of panic may be present against the background of poor breathing.

Methods for diagnosing obstructive bronchitis
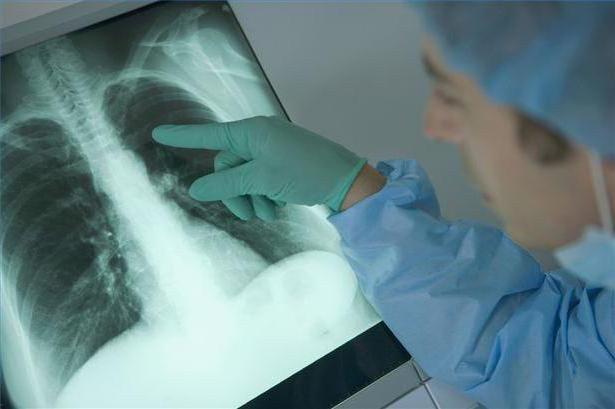
This disease is diagnosed simply. The first indicator of obstructive bronchitis is its symptoms. Characteristic moist wheezing and whistle without problems are determined at the time of auscultation (listening to breathing with a stethoscope).
After that, to confirm the diagnosis, radiography is performed. In the picture, it is possible to accurately determine the degree of damage to the bronchi. In addition, additional diagnostic procedures are shown to the patient to obtain a complete picture:
- Spirography is a hardware determination of the speed and volume of inspiration and exhalation.
- Biopsy of bronchial tissue - is carried out if it is impossible to determine the pathogen of obstructive bronchitis and ineffectiveness of treatment.
- Pneumotachometry - The procedure allows you to calculate the degree of obstruction of the lower respiratory tract, by the method of quantitative determination of exhaled air liters in a second.
- General analysis of biological fluids - examine urine, venous blood and sputum.
Complex diagnosis makes it possible to really assess the degree of damage to the bronchi, determine the presence or absence of changes in bronchial tissues, and the reason that caused inflammation.
Obstructive bronchitis - treatment
Obstructive bronchitis in children is always treated in a hospital, and outpatient treatment is allowed in adults. The therapeutic course is compiled on the basis of the age of the patient, the degree of OFV1, blood indicators, the general condition of the patient.
Principles of treatment of obstructive bronchitis in adults
In order to completely cure obstructive bronchitis in adults, especially if it is chronic, it is primarily determined by its provocateur (this can be smoking, diet, harmful workplace), and then completely isolated.
Out of exacerbation, the treatment involves an increase in immunity, full nutrition, a healthy lifestyle, long -term stay in the fresh air.
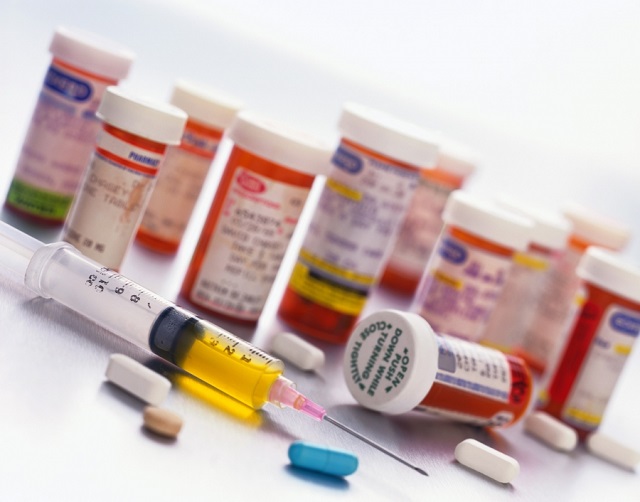
At the time of exacerbation, the patient shows bronchodilators and antibiotics with obstructive bronchitis.
- If the abundant discharge of purulent sputum is determined, antibacterial drugs such as Sumamed, Augmentin, Amoxily can be prescribed.
- To facilitate breathing, bronchodilators are prescribed - an atrovent, Berotek.
- Additionally, drugs contributing to the discharge of sputum - mucaltin, Ambroxol are shown.
- Vibration massage has good efficiency. A set of techniques aimed at relaxing the muscles of the chest is assigned.
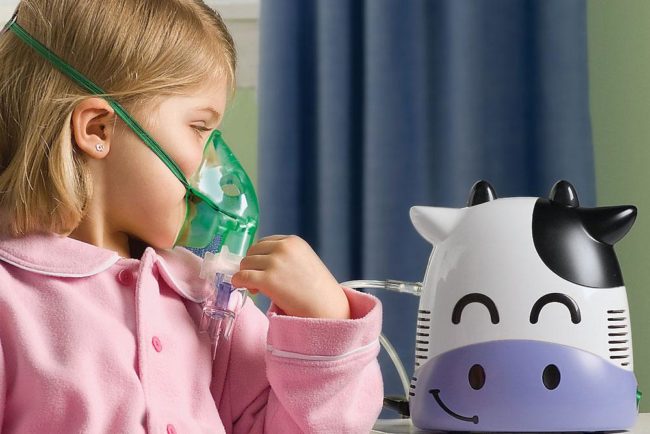
How to treat obstructive bronchitis in children
Treatment of obstructive bronchitis in babies is carried out exclusively in the hospital. Tactics of treatment consists of several compulsory points:
- inhalations - with obstructive bronchitis, it is recommended to use a nebulizer with the introduction of bronchodiating drugs with saline;
- drinking regime - the minimum fluid consumption per day is increasing to ensure a full discharge of sputum;
- antibiotic therapy - is indicated for the infectious cause of obstructive bronchitis and is considered only by the attending physician. The advantage is given to drugs from the macrolide group;
- bronchodilators - prescribed to restore the respiratory function. It can be salbutamol, Berodual, atores;
- mucolics - help sputum to go out, but during the blockage of the bronchi, their purpose is contraindicated. With the permission of the doctor, you can take ACC, Mukhaltin, Lazolvan;
- infusions with vitamins, glucose, anti -shock solutions are relevant with a long and complicated course of the disease against the background of the child’s complete refusal of food and drinking;
- antihistamines - are prescribed in the presence of an allergic component (diazolin, luratidine, erius),
An important place occupies in the treatment of children walking in fresh, preferably wet air. But a logical question immediately arises: is it possible to walk with obstructive bronchitis in children? The answer is positive, but provided that the child does not have high temperature, and there is no severe frost on the street (it is allowed to go out to -10 ° C).

Obstructive bronchitis - folk treatment
There are many effective folk recipes that help remove the edema of the bronchi, improve mucus discharge, and relieve inflammation. Here are a few of them:
- A decoction of elecampane: pour 1 tsp. Raw materials into an enamel container, pour 200 ml of boiling water there, put on a small fire. After 15 minutes, set aside the decoction, let it brew for 3-4 hours, strain. You need to take 1 tbsp. l. 4 times a day.
- Radish with honey: in a black radish, make a recess that corresponds to 1 tsp. honey. Put honey in a hole, wait until the juice begins to ooze from the radish. Per day you need to take 4 tsp. raw materials, with an interval of 3 hours.
- Mandarin infusion: take 25 g of dry mandarin peel and 500 ml of water, place the ingredients in an enamel container, put to cook. In an hour, add another 25 g of tangerine centers, boil the decoction for another hour. Then cool and take it like this: 5 tbsp. l. In the morning, and then every hour one spoon is less. Thus, after four hours you need to drink only 1 tbsp. l. The course of treatment is 5 days.

Contact the doctor in time, take care of your health and remember that it is impossible to cure obstructive bronchitis yourself.








Comments
a couple of years ago, there was no side of metrogils from the same problem, there were no side effects ...
I’m not a fan of peeling at all, it saves from acne of metrogil, it also smoothes it ...
Great article! ...
I take the second course of the Capsules Climafite 911. The tides went very quickly. It became calmer, irritability went away and I sleep well ...
i also noticed - it is worth nervous, everything immediately affects the face. Therefore, I try to avoid conflicts and unpleasant people. Of the creams, I like Miaflow from wrinkles - smoothes not only small wrinkles ...