Unfortunately, even strong bones of the skull are not always able to protect the human brain from various kinds of damage. The traumatic brain injuries can have a serious negative impact not only on the well-being of a person, but also on the quality of life in general. The lightest form of the CTM is a concussion. This type of damage is obtained by both adults and children. How dangerous is this trauma, how to timely and correctly diagnose damage, can a concussion can cause harm to health in general?
Content
Breeding of the brain
The term “concussion” is familiar to almost everyone, but what is really hiding behind him?
ZchMT: A concussion of the brain - what is it
A concussion of the brain is a reversible violation of the functioning of the brain as a result of mechanical injuries. The concept of “concussion” implies a violation of the normal functioning of nerve cells as a result - damage to the connections between them. This type of injury occupies a leading position among traumatic brain injuries. According to the international classifier, ICD-10, the concussion of the brain also fell into this list with personal code S06.0.
In the physiological state, the brain “floats” in the cerebrospinal fluid. As a result of the blow, a sharp impetus of the brain occurs. The pressure of the fluid between the brain and the inner cranial wall on one side increases. At this time, negative pressure occurs from the other side. As a result, the brain receives a hydraulic (and with a strong push and mechanical) blow. Also, rotational displacements of the brain around the axis are possible. One of the most important factors in the differentiation of the ChMT in the diagnosis of “concussion of the brain” is the lack of morphological changes in the brain tissue (hemorrhages of any intensity, violations of circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, ischemia). With mild concussion, there are no serious damage, the negative consequences in the brain are also not noted, the recovery period takes no more than 2 weeks. More severe damage without fail requires the use of drug therapy.
Risk factors for injury - concussion of the brain
What mechanical influences and damage can violate (albeit shortly) normal functioning of the brain? The most common cause of the injury is a direct blow (bruise) on the head. However, damage can also provoke a sharp acceleration or inhibition, in which a sharp movement of the head occurs. They can provoke an injury:
- The bruise received in everyday life, during sports training, due to an accident, during a fight or as a result of a blunt blow.
- A sharp movement of the head as a result of a jump from a height, sharp braking of the car. As for infants, even excessively intense motion sickness can provoke a concussion.

Breaks of the brain: symptoms of the injury
Regardless of the presence and severity of the signs listed below, the fact of an injury should be made to take health more carefully. The following symptoms are the most common manifestations of the concussion of the brain in the adult:
- Headache, dizziness.
- General weakness, pallor of the skin (face), increased sweating of the palms, feet.
- Nausea, in some cases, vomiting.
- Noise in the ears.
- Slide problems, loss of appetite.
- Violation of spatial orientation, inhibition.
- Vegetative disorders are often noted - a violation of the gastrointestinal motility, fluctuations in blood pressure (most often hypotension), a disturbance of the pulse and breathing.
- Partial (retrograde) or complete memory of memory.
In the presence of adequate therapy and successful dynamics of treatment, the listed signs of the concussion of the brain take place within 1-2 weeks. If a negative picture is preserved and after this time, most likely, there are complications or these are the consequences of untimely treatment.

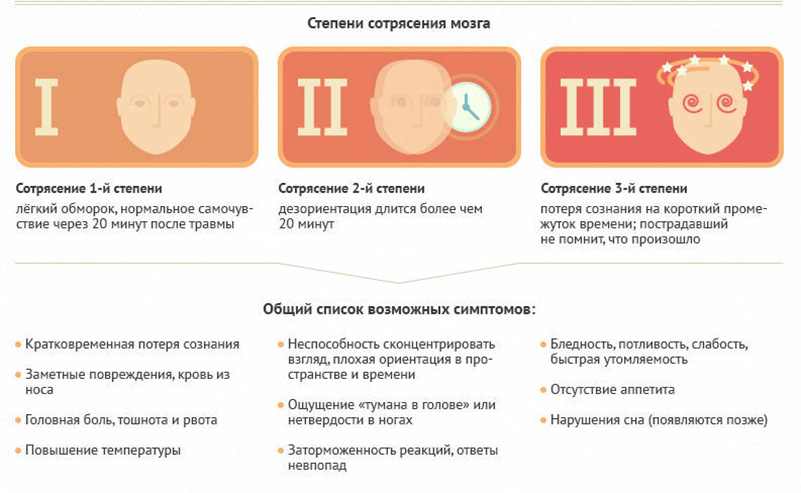
The degree of concussion of the brain
Depending on the severity of the injuries, as well as the severity of the clinical manifestations of the disease, several degrees of concussion are distinguished:
- Light (first) degree. There is no loss of consciousness. Symptoms - disorientation, dizziness, nausea - are weak, present during the first 20 minutes after the injury. Further, well -being comes back to normal. For some time, subfebrile temperature may remain. When diagnosing a slight form of concussion of the brain, treatment can be carried out at home with the recommendation of bed rest for at least the next 2 days.
- Average (second) degree. Loss of consciousness was also not observed, but pathological symptoms are present - confusion, loss of orientation, dizziness, nausea. Signs of damage do not pass even after 20 minutes. Partial amnesia may be observed. The duration of the bed regime is at least a week.
- Severe (third) degree. It is characterized by an obligatory loss of consciousness (even for a short period of time), amnesia (partial or complete), a violation of well-being persists up to 2 weeks.
If, after the injury, a person is in an unconscious state for more than 6 hours, a possible concussion is excluded, because Brain tissue is damaged.
Diagnosis of the concussion of the brain
An adequate assessment of the condition of the victim is one of the most important components of successful therapy for the disease. The following techniques are used to diagnose brain damage:
- The study of the circumstances of the incident, as a result of which an injury was received.
- Inspection of the victim is an attentive examination of traces of bruises.
- The patient's eye bottom is examined.
- Assessment of the psychoemotional state of the patient, the presence of alcohol intoxication.
The doctor gives an assessment to such factors as: or not loss of consciousness, whether there is a violation of the vestibular apparatus, a complaint about double eyes. The diagnosis is established as a result of a comprehensive analysis of the data obtained as a result of such an examination. There are no special diagnostic devices to determine the concussion. It is not possible to establish the fact of a concussion in the usual ways, but often additional examinations are carried out to exclude more serious damage.
- Ultrasound diagnosis determines the displacement or expansion of the structures of the brain.
- Based on the results of CT and MRI, the presence or absence of brain damage is evaluated.
- X -ray allows you to identify possible damage to the bones of the skull.
- Lumbal puncture allows you to set the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid, exclude subarachnoid bleeding.
If additional examinations have not revealed deviations, and the clinical picture and circumstances of the incident indicate an injury, a conclusion is made on the concussion. Do not self -medicate and self -diagnosis, because The restoration of the normal functioning of the brain after improper or insufficient treatment will be even more complex and long. You can suspect a concussion by the following manifestations (after a bruise of the head):
- Headaches, confusion of consciousness.
- Nasal bleeding.
- Extended pupils, fear of bright light and loud sounds.
- Nausea, vomiting.
In the presence of these signs, it is necessary to immediately contact the medical institution.

Breaking Brain Breaking through: Trauma treatment
Therapy in the case of diagnosing a concussion should be complex. Its intensity directly depends on the degree of defeat.
Light concussion
So with a mild degree of concussion, treatment of the house is allowed, but only with the permission of the doctor. Main recommendations:
- Bed rest, long sleep.
- During wakefulness, it is allowed to listen to music (but not through headphones).
- It is necessary to adhere to a lactative diet with minimal inclusion of table salt.
- Herbal soothing teas, as well as infusions, are used as therapeutic agents.

Treatment of a concussion of the brain in adults with concussion of the second and third degree
More serious injuries are not dispensed with without drug treatment and the patient’s premises in the hospital. After three days, the doctor makes a conclusion about the possibility of transferring the patient to outpatient treatment. What drugs are used for treatment for concussion?
- Anesthetics - Baralgin, Ketorol, Sedalgin.
- Antipsychotics (to improve blood circulation in brain structures, accelerate metabolism) - piracetam.
- Medicines for improving metabolism in tissues, antioxidants - Mexidol, Mexpime.
- Means to prevent and reduce cerebral puffiness - Cavinton, Eufillin, Sermion, Trental.
- Soothing and sleeping pills, the purpose of which from the concussion of the brain is justified - Finlepsin, phenobarbital, glycine.
- Anticonvulsants - nosepam, tincture of hawthorn, motherwort, phenibut.
The patient is prescribed abundant drink-up to 3 liters of water per day, vitamins B and C, magnesium, omega-3. If, after the course of treatment, such symptoms as dizziness, decrease in performance, memory deterioration, increased irritability, additionally prescribed a course of vitamins B are preserved. , Betasserx, sink, tincture of motherwort. In addition, throughout the month after the concussion of the brain, any physical exertion and sports are not allowed. Reading literature, watching television programs and working at a computer should also be postponed.

Help with a concussion
Timely and competently provided first aid avoids complications as a result of the injury. First of all, it is necessary to call an ambulance.
Suffering unconscious with a concussion of the brain
If a person is unconscious, first aid for a concussion of the brain or suspicion of him is to fix his body in the correct position. This is necessary:
- Put the victims in a saving position - on the right side, the head is thrown slightly, the hands and left leg are bent at the knees, the face is turned to the ground. This position provides reliable fixation of the body, free air flow into the lungs, when the vomiting of vomiting, the risk of choosing a minimum is minimized.
- On bleeding wounds, if this is present, a bandage is applied.

Suffered in consciousness with a concussion of the brain
If a person is conscious:
- Put it in a horizontal position so that the head towers a little above the body.
- Follow his consciousness and do not let sleep.
- Call the doctors.
Regardless of the severity of the injuries, all patients are placed in a hospital for the first 24 hours after injury.
Breeding of the brain in a child
Unfortunately, not only adults, but also children are subject to head injuries. Most often, bruises are obtained as a result of increased motor activity by children, some sports. Although there may be a consequence of an accident or fight. Kids up to a year age are also at risk - inattention from the parents leads to the fall of the crumbs from the crib, a changing table, and strollers. The fall even from a small height can provoke a concussion.
Symptoms of the concussion of the brain in children
The clinical manifestations of the concussion in children differ from adult symptoms, and the growth of symptoms also occurs faster. The insufficient maturity of the brain tissue, the incompleteness of the ossification and complete fusion of the bones of the skull, the instability of the vascular system lead to the rapid disappearance of the manifestations of a concussion - a few hours after the injury, neurological symptoms may completely go down. In children from birth to 3 years, a suspicion of the presence of a concussion should cause the following signs:
- The kid does not lose consciousness.
- There is a sharp turning of the skin (immediately after the blow).
- The rapid heartbeat (immediately after the injury) is replaced by lethargy, drowsiness.
- It can swell the fontanel (in infants).
- If the baby is breastfeeding may be noted by spraying during feeding, vomiting, and increased anxiety.
- Sleep violation.

In older children (preschool and primary school age), the picture is more often as follows:
- Loss of consciousness is most often absent.
- Sweating is noted, blood flow to the face.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- “Jumps” pressure and pulse “jumps”.
- A child can complain about headaches.
- There is a disorder of sleep and appetite.

How to treat a concussion in a child
The first thing to do in the event of a head injury is to call an ambulance. Timely, competent therapy begun to minimize or prevent the development of complications at all. Before the arrival of doctors, it is necessary to maintain the wakefulness of the child. If he is unconscious, put him in a saving position (just like an adult) and expect the arrival of doctors. The examination of the child does not differ from the diagnostic procedures for an adult. If drug therapy is required, the following drugs can be prescribed in childhood with a concussion:
- To prevent edema of the brain substance, drugs with a diuretic effect are prescribed - diacarb, furosemide, as well as potassium preparations - panangin.
- Single (sedative) means - phenosepam.
- Antihistamines, for example, zodak.
- Anticonvulsant drugs.
- A complex of multivitamins permitted by age.
If an adult patient, depending on the seriousness of the injury, can be transferred to outpatient treatment after a day, then children are most often left in a hospital for a week (at least three days).
Complications and consequences of the concussion of the brain
The lack of adequate therapy during the resulting concussion threatens the development of dangerous complications, including:
- Strong headaches (migraine).
- Excessive (uncontrolled) emotionality - increased excitement, aggression.
- Convulsions similar to epilepsy attacks.
- State of anxiety, fear.
- Insomnia.
- Sustainable asthenic syndrome.
- Rarely, but psychoses, dementia, disorientation in reality are noted, leading to disability.
However, even if the treatment was prescribed in a timely manner and passed successfully, for a long time after a concussion of the brain, a number of patients notes headaches, memory impairment (poor assimilation of information), a decrease in concentration, increased irritability, sleep disturbance.









Comments
a couple of years ago, there was no side of metrogils from the same problem, there were no side effects ...
I’m not a fan of peeling at all, it saves from acne of metrogil, it also smoothes it ...
Great article! ...
I take the second course of the Capsules Climafite 911. The tides went very quickly. It became calmer, irritability went away and I sleep well ...
i also noticed - it is worth nervous, everything immediately affects the face. Therefore, I try to avoid conflicts and unpleasant people. Of the creams, I like Miaflow from wrinkles - smoothes not only small wrinkles ...