Otite is a fairly common ENT pathology that affects both children and adults. It is characterized by the presence of pain, congestion of the ear, a decrease in hearing acuity and many other symptoms. Very often otitis media of the middle ear manifests itself in infants, then the kids cry at night, causing anxiety among their parents. It is important to start the treatment of this disease in time in order to reduce not only unpleasant symptoms, but also to prevent the development of complications, which is especially dangerous in childhood. Next, we consider in more detail the characteristics of this pathology, as well as what to do with otitis media.
Content
Otite of the middle ear: symptoms
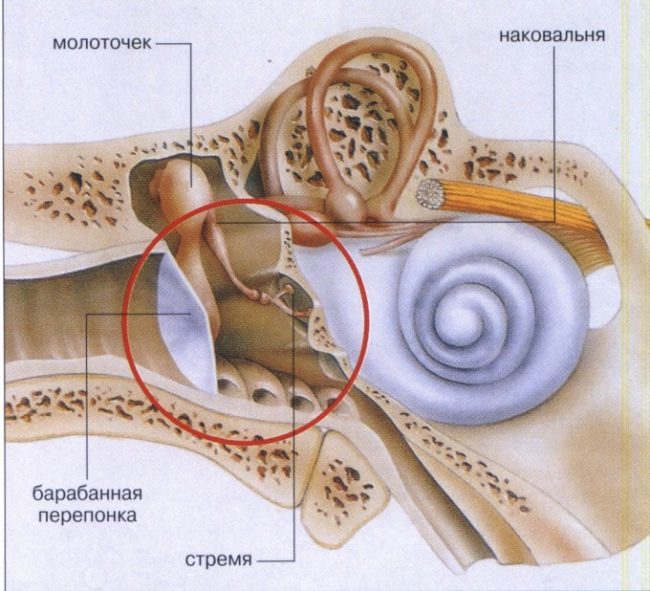
Otitis of the middle ear is characterized by the presence of an inflammatory process, which most often develops as a result of the penetration of various malicious bacteria and infection into the ear cavity. The disease develops quite quickly and rapidly. Pain in this case arises both in the area of \u200b\u200bthe temporal bone and in the area of \u200b\u200bthe auditory passage. Often the inflammatory process from the middle ear is also extends to the Eustachian pipe.
This disease is diagnosed in 25-30% of all patients seeking help to ENT doctors. In addition, about 60% of all babies aged 1 month to 3 years suffer from this ailment.
Symptoms of the middle ear in adults and children are as follows:
- Pain in the temporal region and in the area of \u200b\u200bthe auditory passage. The pain can be of different - pulsating, shooting or aching nature. Sometimes unpleasant sensations can be given to the back of the head, as well as with otitis media, teeth located on the side where the sore ear may hurt.
- Reducing the acuteness of hearing. Hearing in patients can worsen both at the very beginning of the occurrence of the disease and in the case of its progression.
- Feeling of ear congestion. Often the patient experiences unpleasant sensations of congestion in the middle ear.
- Sometimes the patient can complain that he hears resonation (echo) of his own voice in his ear during a conversation. This symptom is called in medical practice as autofonia.
- The presence of noise and extraneous sounds in the ear.
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes located closest to the amazed ear.
- The presence of discharge from the auditory pass that has a purulent or serous nature.
- Sometimes the patient has edema in the earlier area.
- A patient with otitis media often has an increase in temperature above 38 degrees.

- General weakness, drowsiness. Since the pain with otitis media is pronounced in nature, the patient is impaired, irritability appears, appetite decreases.
Otite of the middle ear: reasons
There are many reasons that can provoke the onset of this serious disease:
- Most often (in 70% of cases) the disease occurs as a result of the action of harmful bacteria and microorganisms, for example, such as streptococci and staphylococci.
- Sometimes the cause of the development of the disease is improper smoking, in which the air pressure on the auditory passage is unevenly distributed.
- Nose diseases (for example, adenoids, curvature of the nasal septum, catarrhal rhinitis).
- The abnormal structure of the nasal shells, in which their rear edge prevents the normal opening of the auditory pipe.
- Infectious diseases of the nasopharynx.
- Injury to the Eustachian pipe, eardrum, and auditory passage.
- Various tumor formations located in the nasopharynx.
- Colds caused by hypothermia of the body (sore throat, flu, etc.).
Acute otitis medium
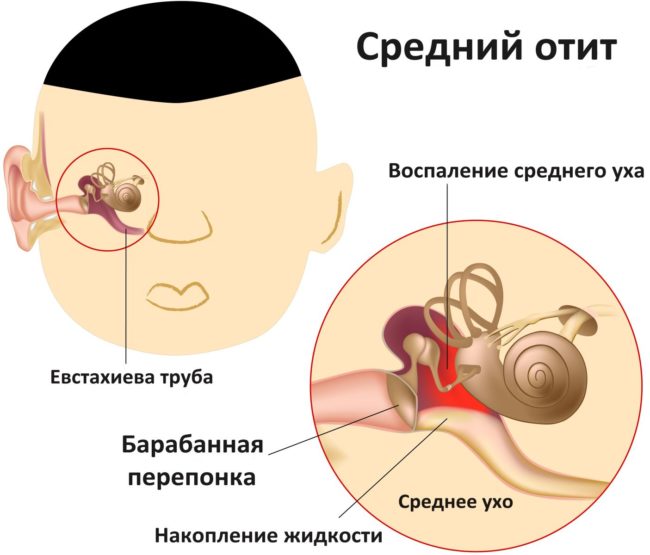
Distinguish between chronic and acute otitis media. The acute inflammatory process proceeds in several stages:
- The initial degree of the disease. In medical practice, this stage is called a prefortive one. At this stage, the disease proceeds rapidly, the general symptoms of the disease increase and become pronounced. The presence of severe pain in the ear area is noted. The pain is often pulsating and acute. Pain spread to the ear, and occipital region. This stage can last 1-2 hours and several days. It all depends on the action of the body's immune system, as well as on how much the infection of the middle ear occurred. At the initial stage, purulent discharge intensively accumulates and focuses in the area of \u200b\u200bthe auditory passage. This stage of the disease can diagnose an ENT doctor using a visual examination of the patient's auditory passage. Typically, in this case, a thickening of the eardrum is noted.
- Perforative degree. This stage of the disease is very serious, since in this case the accumulated purulent discharge can break through the eardrum. At the same time, pain is pronounced in nature and extend not only to the ear area, but also to the temporal, occipital part, and also hung up in the upper and lower jaw (the patient's teeth begin to hurt). At this stage, there is an increase in the patient’s body temperature to 38 degrees. The duration of this stage of the disease is from 1 to 8 days.
- Reparative stage. The final stage of the disease. In the case of proper and adequate treatment, scarring of the broken parts of the eardrum, the amount of purulent contents secreted, is reduced, the patient's hearing is restored.
Chronic otitis media
Chronic otitis media of the middle ear flows languidly and slowly. Very often this disease develops as a complication after improper treatment of an acute infectious process. In this case, the mucous membrane in the auditory passage and in the eardrous cavity is inflamed and swells.
The chronic process is characterized by the presence of the following symptoms in the patient:
- First of all, the quality of hearing worsens.
- Patients note the presence of periodic noise and buzzing in the ears.
- Headaches of periodic in nature.
- Dizziness.
- Periodically, the presence of serous discharge from the auditory passage is possible.
Otitis - inflammation of the middle ear: types of disease and their diagnosis
Exudative otitis media
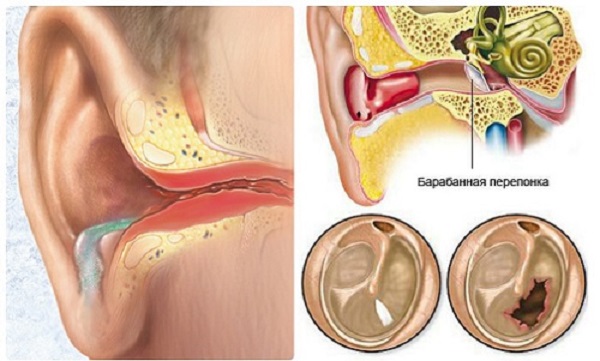
The exudative otitis media of the middle ear is characterized by the presence of serous discharge in the auditory passage. This type of disease is most difficult to identify in the patient, since with exudative otitis media there are no pain in the earlier and temporal region. At the same time, the patient does not increase the temperature, and the integrity of the eardrum is also preserved. Most often, this type of otitis media is a consequence of the course of various inflammatory ENT pains.
Catarrhal otitis medium
The catarrhal otitis media of the middle ear is rapidly. With this type of disease, a person has a pronounced pain, as well as an auditory passage and a mosque process. If acute catarrhal otitis media cannot be cured in a timely manner, then the patient can completely lose his hearing. The causes of the development of the disease in this case are the presence of adenoids, a curved nasal septum. In addition, this type of otitis media can develop with a general decrease in immunity, insufficient consumption of vitamins with food.
Purulent otitis medium
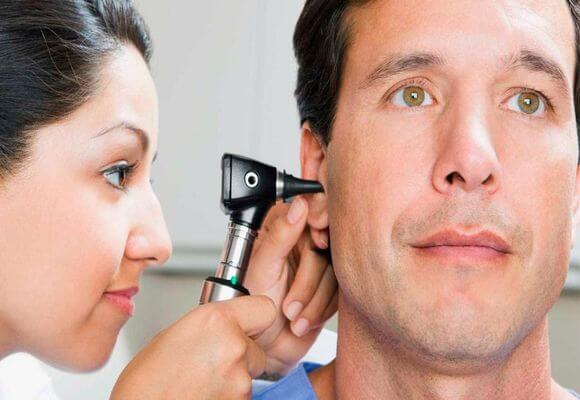
Purulent otitis media of the middle ear is an acute inflammatory process. In this case, the patient has the presence of pain, not only in the area of \u200b\u200bthe auditory passage, but also in the temporal, as well as in the earlier area. Pain can be given to the back of the head, lower jaw. There is an increase in body temperature to 39 degrees. If this pathology is not treated, the patient, as in the case of catarrhal otitis media, may completely lose hearing. Complications after this form of otitis media can be brain sepsis, meningitis.
Serous otitis media
Serosa otitis media of the middle ear is an inflammatory process that has weak symptoms. In this case, liquid accumulates in the auditory passage without pus impurities. Due to the abundance of savings, the patient may experience a sensation of pressure in the middle ear. The hearing at the same time decreases slightly. The body temperature rises moderately, no more than 38 degrees.
Adhesive average otitis media
Adhesive average otitis media is a form of chronic otitis media. In this case, the symptoms of the disease in the patient are poorly expressed. The only thing that patients note is a significant decrease in hearing.
Otitis media in children
As mentioned above, most often this disease is diagnosed in infants, as well as in children under 3 years of age. The main causes of otitis media in children can be the following factors:
- Colds, flu.
- The presence of a long runway, as a result of which the infection with the nasal sinuses passes to the middle ear.
- Hypothermia of the body.
- The penetration of infection directly into the ear cavity when bathing a child.
The main symptoms of otitis media in children:
- The presence of a high temperature is up to 39 degrees.
- Raping the head from infants while crying.
- The presence of pain in the earlier and temporal region.
- Refusal of food, lack of appetite.
- Vomit.
- Reducing the quality of hearing, a sense of congestion in the ears.
How to treat otitis media in the middle ear:
- First of all, you need to remove the pain in the kids. For this, drugs such as Nurofen, Ibuprofen, I have, Panadol, Calpol are suitable.
- Next, you should gradually remove the inflammatory process in the middle ear with the help of such drops as Otipax, Otinum (1 drop twice a day). You can bury 3%boron alcohol in the baby's ear.
- In addition, you should constantly clean the baby’s nasal passages from the discharge.
- Swelling in the nasal cavity can be removed using drops - “Nazivin”, “Nazol”, “Nogspre”, “Vibration”.
Otitis medium ear: treatment
Antibiotics with otitis medium ear

In the treatment of this disease, the cause that caused otitis media ear should first be eliminated. And since most often the disease occurs due to the effects of harmful bacteria and microorganisms, patients need antibiotics.
Antibiotics with otitis media:
- Levomycetin. It is used for purulent otitis media. In a sore ear should be instilled 2 drops.
- Amoxicillin. It is used 3-3.2 g per day.
- Augmentin. It is prescribed to both adults and children. Adults 350 mg 2 times a day.
- Ceftriaxone. It is used once a day.
- Amoxicillin. It is used 2 times a day.
- Amoxiclav. It is used 2 times a day.
Otitis medium ear: drops
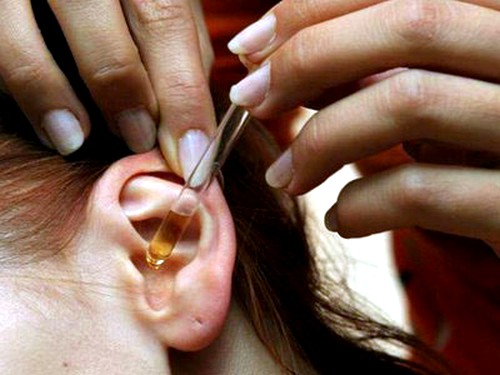
Most often, drops are used with otitis media. Their action is aimed at removing the inflammatory process in the auditory passage. In addition, some drugs can significantly reduce pain.
So, with otitis medium ear, the following drops are used:
- Otipax. Drink 1-2 drops in each ear.
- Otinum. For children, 1 drop in a sore ear is enough. Adults will need 2 drops twice a day.
- Anauran. This drug is instilled 1-2 drops into the affected ear.
In addition, with otitis media, you should use nasal drops that relieve inflammation in the nasal passage and improve its cross -country ability. Such drugs include:
- Tizin.
- Otrivin.
- Nazivin.
Otite of the middle ear: folk remedies
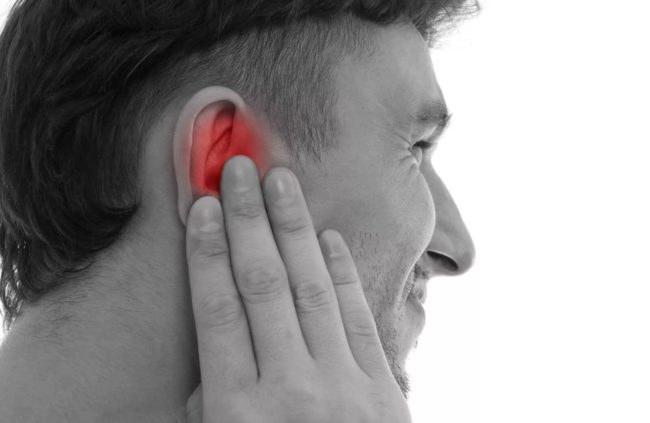
Consider how to treat otitis media at home with the help of traditional medicine. These recipes include the following:
- Juice of onions and garlic. In this case, only freshly squeezed juice is used. It should be diluted with clean boiled water in a ratio of 1 to 1, and then dig 1 drop into the sore ear.
- Aloe. It has intense anti -inflammatory properties. With otitis media, a cotton swab is moistened in aloe juice and it is laid in the affected ear for 5 minutes 1 time per day.
- Kalanchoe. The juice of this plant has the same amazing properties as aloe juice. In this case, a cotton swab is similarly used, which is moistened in freshly squeezed juice, and then placed in a sore ear.
- Propolis tincture. It can be used in the same way as boron alcohol. In this case, the propolis tincture is buried 1-2 drops in each ear.








Comments
a couple of years ago, there was no side of metrogils from the same problem, there were no side effects ...
I’m not a fan of peeling at all, it saves from acne of metrogil, it also smoothes it ...
Great article! ...
I take the second course of the Capsules Climafite 911. The tides went very quickly. It became calmer, irritability went away and I sleep well ...
i also noticed - it is worth nervous, everything immediately affects the face. Therefore, I try to avoid conflicts and unpleasant people. Of the creams, I like Miaflow from wrinkles - smoothes not only small wrinkles ...