According to scientific research, most of our thoughts are unconscious and repeated daily in different versions. But sometimes a person has a condition in which he is fixated on any one thought, all the time returns to her, tries to allow, experiencing the same experiences. An obsessive internal dialogue is spinning in my head, which leads to fatigue and emotional emptiness. As a result, in addition to the obsessive thoughts themselves, a person has a fear of waiting for them.
Content
Obsessive thoughts - types, psychology, methods of struggle

Simply put, obsessive thoughts are thoughts that are not amenable to our management. They can be described as a monotonous scrolling of one plot in the head, possibly in a different manner.
According to the classification of Yasper, all obsessive thoughts are divided into two main groups.
Abstracts who do not lead to any fears:
- obsessing the need for the account of something (arifomania);
- unnecessary division of sentences into words or words into syllables;
- telling your own memories on an ongoing basis;
- multiple (resonance).
Figurative, causing anxiety states:
- painful experience of the events of the past;
- doubts, uncertainty in anything;
- desire to do indecent things;
- fears for the commission of incorrect actions.
It is such obsessive thoughts that poison human consciousness, interfering with enjoying life.
Obsessive thoughts in the head are associated with such emotions:
- resentment;
- fear;
- a feeling of guilt;
- anger;
- complexes;
- anxiety.
On the other hand, obsessive thoughts perform a positive function:
- indicate unresolved problems;
- spend, a kind, subconscious attempt to find a way out of a difficult situation;
- promote concentration on solving the problems that excites us.
However, it must be remembered that such fears can be caused by both natural, real, reasons, and absurd, illogical. At the same time, a person understands their far -fetchedness, but does not know how to get rid of them.
Obsessive thoughts in the head can lead to:
- insomnia;
- anxious state;
- reducing productivity due to the fact that they distract a person;
- generation of new complexes.
Before trying to remove obsessive fears, figure it out first if they have a base, and what is the probability that an event is frightening. Do not ignore the problem of their occurrence. Even if she is too exaggerated, she is still. In other words, when you are worried about having a terrible illness, go to the doctor and examine.
In addition, pay attention to what circumstances accompany your obsessive thoughts:
- intellectual unnoticed (constant staying at home, incomplete workload at work, automatic actions) - in this case, be sure to take yourself, find a hobby, engage in self -development;
- constant stress (lack of time, chronic fatigue, lack of sleep, excessive workload) - in this state it is necessary to force yourself to relax and change the picture.

Psychologists offer many ways and methods that help get rid of obsessive thoughts:
- if fears appear, write them down in the slightest detail. Having gained the material form of words, they will seem meaningless;
- analyze obsessive thoughts in order to understand what is the reason for their appearance. If negative experiences took place in your past, think about how your life has changed from that moment, and what is the likelihood of a repetition of a similar situation;
- live reality, concentrating on those events that delight you;
- if you are covered by panic fear in a public place, switch your attention to some passerby and imagine what he thinks where he is going, etc.;
- imagine the worst version of your script scaring you. Mentally humble yourself with him and try to find a way out of such a situation;
- visualize an obsessive thought and imagine it in the form of a deceiver who wants to mislead you. Clearly say that you showed it off and then do not pay attention to it;
- if possible, change some life circumstances to deprive of the fear of its relevance (with a fear of public transport - acquire a personal car, with a fear of heights - settled on the lower floor). However, this method does not relieve fear itself, but only allows you to make life more comfortable;
- sprinkle your fears and obsessive thoughts. Express them in a laconic form and sing. This method may seem ridiculous, but it is quite effective, since an ironic attitude to obsessive thoughts contributes to their disappearance;
- twice a day, allocate a certain amount of time (no more than 10 minutes) for conscious pondering obsessive fears. In this case, it is necessary to maximize the negative sensations, avoiding any possible positive solution. The human psyche is able to withstand such a blow only a limited time, and then protective functions are included. As a result, the anxiety will gradually decline, and the time allotted for fear will be filled with boredom. Obsessive fears will seem already experienced and obsolete;
- spend more time in public places, visit parties, exhibitions. Forced communication with people will distract from obsessive thoughts;
- use the following respiratory equipment. Imagine your obsessive thoughts or fear in the form of an image. Inhale slowly and deeply, and then quickly exhale, imagining that, together with the exhalation, you save your body from an obsessive idea. Repeat such an exercise several times a day;
- replace negative ideas positive. To do this, write down on paper, obsessive thoughts that disturb you. On another sheet, describe a positive option, replacing them with anxiety and experience. Carry this leaf with you or write down the words on the recorder. Every time a sad thought appears in your head, read or listen to your positive attitude.
Some psychologists consider it the best way to get rid of obsessive thoughts - not to fight them. Because when you try not to think about obsessive fears, you already think about them. By resisting, you strengthen internal emotional stress.
And indifference to their annoying thoughts leads to the fact that they leave our consciousness.
The essence of this method:
- do not enter into the fight against obsessive thoughts. Let them be present in your mind. Do not do the analysis, do not start dialogue, but just observe. Always remember that these are just thoughts, and you are not obliged to believe them;
- listen to the sensations that appear in your body. Allow yourself to accept them and feel completely, even though at first it will be difficult. Over time, these painful symptoms will be weakened, and after that they will disappear at all;
- slowly translate your attention to the breath, breathing and exhale deeply and slowly. This will restore the strength of the body;
- consciously switch to the reality surrounding you: sounds, tactile sensations, smells. So you will plunge into the real world.
Belief, when you change your own attitude to this situation, your fears will gradually weaken, and then disappear, because they will not be endowed with emotional acuteness.
Some warnings in eliminating obsessive thoughts:
- take your time. Let everything go on as usual. Accept the installation: there are no obsessive thoughts - good, and if they are still present - nothing to worry about;
- do not talk about your obsessions to outsiders (except for doctors - specialists), since this is once again reminding yourself of the problem. In addition, subsequently, when you begin to get rid of your anxieties, your acquaintance, showing interest, may by chance remind you of your fears and thereby destroy the acquired balance;
- do not be discouraged if a positive result does not come quickly. It is impossible to accurately determine how much time you need for this. Expecting impatiently getting rid of obsessive thoughts, you thereby concentrate on them;
- do not be afraid that the rejection of analysis and internal monologues will deprive you of the opportunity to solve the problem. This is a deceptive impression. After all, having allowed one doubt, your anxious mind will immediately throw the following;
- forget that you must always control your thoughts and bear responsibility for them. Accept the fact that in our life not everything depends on us;
- do not reproach yourself for visiting obsessive thoughts that are, as it seems to you, shameful or terrible. The main thing is not our thoughts, but how we use them;
- use relaxation methods;
- avoid darkness and twilight in the room. It is proved that bright light enhances the production of serotonin (hormone of pleasure).
Keep in mind that obsessive thoughts will sometimes return to you. Do not scare it. Try to smoothly take your thinking in the other direction. Remind yourself that they are just an ordinary illusion born of a brain.
Outdoor thoughts
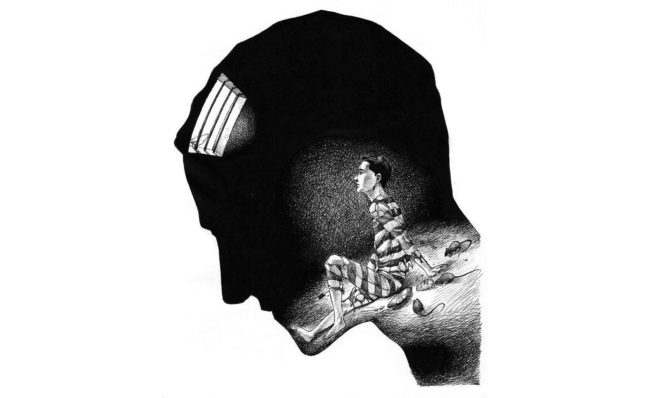
Enough thinking is characterized by each of us. Throughout life, we all experience anxiety, fears and other negative experiences. This process is quite natural. However, it happens that such a state is delayed, prevents the fully live and develops into a nervous or mental disorder - obsessive thoughts syndrome.
Scientificly obsessive conditions are called obsessive - compulsive disorder (OCR):
- obsession - an obsessive thought, alien to the patient and causing anxiety;
- compulsion - a stereotypically repeated action caused by an obsession.
The pathology is not the very content of negative thoughts, but their dominant nature and inability to get rid of them.
Neurosis of obsessive thoughts is a state when a person has a feeling of presence in the head of some information that is repeated repeatedly and thereby burdens consciousness.
The occurrence of neurosis can be described as follows:
- fear (real or imaginary) appears in the mind, as a result of which the patient loses self -confidence;
- having rooted, fear causes negative thoughts that acquire a chronic form.
This disorder has different intensity. The following forms are distinguished:
- one -time - the neurosis lasts for a certain (sometimes sufficiently long) time at the same level;
- remitive - symptoms periodically fading or exacerbated;
- progressive - fears exacerbate and grow.
The methodology of this ailment is contradictory and not sufficiently studied, so the diagnosis often causes panic. However, a person who has discovered symptoms of obsessive thoughts neurosis should not be ashamed or afraid of it. Do not confuse neurosis with psychosis. Simply put, you are not crazy. Your doubts and the desire to get rid of this state are proof that you have precisely a nervous disorder, and not a mental one.
Symptoms of obsessive thought neurosis are:
- scrolling in the head of repeated obsessive painful images;
- phobias of various nature;
- constantly pop -up phrases, lines from songs;
- a return to the memories that cause shame;
- doubts about the decisions made or committed;
- hallucinations (rarely quite);
- continuous internal dialogs;
- impulsive motives to harm yourself or others (step from the roof, rush under the wheels or push a passerby under them) and fear like that;
- hyperperfecmentism (a person cannot stand the mess and even at a party begins to correct and wipe everything);
- obsessive thoughts of an intimate nature.

Sometimes obsessions lead to obsessive actions (compulsions):
- inventing the ritual (to leave the house only from the right leg or count the trees on the way to work);
- deliberately avoiding places and situations causing fear (abandoning knives due to fear of cuts, bypassing the places where there was an attack of panic);
- a complete assignment on external assistance (medicines, friends, relatives);
- involuntary movements (sniffing with a nose, biting nails, swinging with a foot).
This behavior is a kind of protection against obsessive thoughts and anxieties. But over time, this problem is aggravated, since such things only remind a person of his fears and contribute to the complete loss of control over the situation.
People suffering from obsessive thoughts syndrome:
- experience difficulties in communication;
- are in a state of depression;
- completely immersed in the invented world of his fears;
- prone to aggression.
In addition, this disorder can have a negative effect on human physiology, causing:
- vegetovascular dystonia;
- enhanced intestinal motility;
- dizziness;
- shortness of breath;
- increased sweating;
- nausea;
- heart rhythm disturbances.
A feature of such an ailment is that the patient is aware of his condition, but is not able to cope with him on his own. In order to get rid of neurosis of obsessive thoughts, you need to understand the reasons for its appearance, the main of which are:
- the presence of strict beliefs, attitudes and unshakable faith in them;
- a personal feature of thinking, which consists in an alarming perception of oneself and the surrounding world. A tendency to exaggeration and nervous disorders;
- the habit of conducting an internal dialogue (often emerges in childhood, when the child rehearses an acquittal in advance for some misconduct);
- the sincere belief that our own fear is inextricable;
- the absence of a loved one with whom you can share or speak out;
- excessive instinct of self -preservation, which protects against dangerous, in understanding our consciousness, situations.
Additional factors that contribute to the development of obsessive thought neurosis can be:
- biological aspects (heredity, disorders of the chemical balance in the brain);
- acute mental trauma;
- alcoholism;
- chronic fatigue;
- nervous and physical exhaustion;
- infectious diseases;
- adverse atmosphere in the family.
Diagnosis of obsessive thought neurosis is carried out as follows:
- the patient is interviewed for complaints and general assessment of personal characteristics;
- the presence of signs of a neuralgic nature (sweating, tremor of the limbs, vegetative problems) is checked;
- close patients are interviewed;
- tests are carried out to determine the degree of nervous disorder and the real need for the help of a doctor.
A significant fact for diagnosis is the daily occurrence of obsessive thoughts or actions that occupy at least an hour a day.
To defeat neurosis of obsessive thoughts, you need to work in two directions:
- mental - in order to adjust thinking (getting rid of false attitudes, elimination of anxiety);
- physical - aimed at restoring the tone and strength of the body (rest, proper nutrition, walking in the fresh air, physical exercises, taking vitamins).
With timely diagnosis, this disease is successfully cured. At the initial stage, most people are able to independently cope with neurosis of obsessive thoughts. But in advanced cases, it is recommended to contact a therapist.
Obsessive thoughts about death

One of the types of nervous disorders is obsessive thoughts of death.
Conventionally, they can be divided into:
- fear of death (tanatophobia) - panic fear of death;
- suicidal - a desire to end life.
Obsessive thoughts - tanatophobia

The main causes of the pathological fear of death:
- the loss of a loved one, as a result of which increased anxiety and loss of mental balance develops;
- negative images of cessation of life created under the influence of films, programs, news;
- fear of punishment for the "sinful" life of very religious people;
- knowledge of himself and the universe, when a person asks questions about the meaning of life and its fleeting;
- reassessment of life principles and priorities, getting rid of illusions and youth plans, “crisis” age period;
- fear of what is not amenable to study;
- life shock (illness, moving, breaking relationships).
I must say that more often people are not afraid of the fact of death, but the circumstances that can accompany it:
- the realization that in life did not have time and did not do;
- absolute oblivion after his departure;
- fear for children or elderly parents, for whom there will be no one to care;
- painful pain with dying;
- loss of dignity from their own incapacity;
- loneliness in the last hours of life.
Some psychologists believe that obsessive thoughts of death most often visit selfish people, whose attention is focused exclusively on themselves, their body and sensations.
You need to understand that disturbing thoughts about death periodically visit all people. This is not a disease yet. You can talk about neurosis when such thoughts become persistent and completely master consciousness.
Sometimes such a pathological fear carries a positive function: a person refuses a meaningless existence and strives for self -improvement.
Ways to overcome obsessive thoughts about death:
- recognize your fear and do not be ashamed of it. Afraid of death is normal. This, a kind of protective mechanism of the body from self -destruction;
- determine the goal in your life and strive for it. Make a plan for self -realization and follow it. Remember the words of philosophers and writers that those who live their lives are not effectively afraid of death;
- find the lesson to your liking, which will take away most of your free time;
- try to avoid communication with people tuned with pessimistic. Bring more positive into your life;
- start and end your day with words of gratitude for everything that life gave you;
- fill every moment of your existence with joyful moments (walk, read, discover new talents in yourself);
- less attention on yourself and your experiences. Think about others, help relatives, take care of charity;
- do not refuse to support loved ones and relatives. More often spend time with those who are dear to you;
- a believer can turn with a prayer to God or talk to a priest;
- remember: no one knows what actually happens after death. This is a secret that is not subject to reveal. Maybe we will get after our departure to where we will be good.
If the obsessive fear of death does not work independently, contact a psychotherapist who will reveal the true cause of a neurosis and help to cope with it.
Obsessive thoughts about suicide

A more serious problem is obsessive suicidal thoughts that mentally healthy people who experience serious conditions can be subject to:
- in deep depression or despair;
- lonely, believe that no one needs them;
- surviving severe mental trauma;
- suffering from exorbitant guilt;
- convinced of the meaninglessness of their own existence;
- lost the meaning of life;
- experiencing constant severe pain (for example, during the period of illness).
The obsessive thoughts about the commission of suicide are not amenable to human control, they torment him, and, accumulating, can lead to tragedy. Therefore, it is extremely important to recognize the problem in time and seek help from close people or specialists.
In cases where you are visited by thoughts about suicide, listen to the advice of psychologists:
- obsessive thoughts come to you from outside, they are not a manifestation of your mind;
- suicide is just an illusion of a way out of a difficult situation;
- there are probably people in your environment who love you or need your care;
- feel free to talk about your experiences and ask for help. Call a hot line or a close friend;
- leave the apartment and go to the society of people - the change of scenery will distract you in addition to your will;
- write a list of everything that pleases you in life: your favorite dishes, the names of friends, pleasant memories. Read it every time painful thoughts appear again;
- do not be too demanding on yourself. Understand that many people found themselves in a similar situation. You have nothing to be ashamed of and blame yourself;
- make a plan for you to do or try. Let it be as many points as possible in it.
Sometimes obsessive thoughts about suicide are a manifestation of various mental disorders:
- schizophrenia;
- endogenous depression;
- delirious state.
In such cases, urgent psychiatric care is required, up to the hospitalization of the patient.
Obsessive thoughts about diseases

More and more people are aware of the need for a correct attitude to their health and timely preventive measures. However, sometimes such concern develops into obsessive fears about the possibility of getting sick - hypochondria or nosophobia (fear of the disease).
Hypochondrock is obsessed with a fear of picked up any unknown virus or incurable disease. Sometimes it is enough for him to read the article or hear that someone was ill, as he immediately finds such symptoms. As a rule, obsessive thoughts of diseases are closely related to the fear of death.
A similar neurosis manifests itself as follows:
- frequent visits to the clinic and conducting multiple medical examinations;
- excessive use of various food additives;
- passion for non -traditional recovery methods;
- avoiding situations and social contacts that can be allegedly caused by the disease.
When an obsessive thoughts about diseases are constantly pouring a person, physiological symptoms may also be manifested in him:
- rash;
- nausea;
- fever;
- tachycardia;
- indigestion;
- somatic pain.
The most common causes of such a neurosis are:
- the transfer of a severe illness in the past by the patients or his relatives;
- personality features (imagination, pessimism, increased impressionability).
Diagnosis of hypochondria and nosophobia is quite difficult, since at first a person complains of pain, which be somatic. A number of examinations are assigned. Then the patient doubts the correctness of the results. Therefore, the analyzes are often prescribed again. In the meantime, the neurosis is progressing. Sometimes there is enough time when, finally, the true cause of the negative condition of the patient is determined.
Obsessive thoughts about diseases prevent the fully live and work, causing a person:
- uncontrolled anxiety in the mention of any ailment;
- the need to do everything possible in order to avoid a clash with the disease;
- awareness of the illogicality and groundlessness of fear and the inability to control it;
- irritability, a feeling of shame and guilt.
To get rid of obsessive thoughts about diseases is real, because we ourselves are responsible for our emotionally - mental state.
One of the effective methods of getting rid of such fears is the creation of the so -called “positive anchor”. The essence of the method is as follows:
- choose a particularly strong memory that causes you extremely positive emotion;
- create an “anchor” - an action that you will use when negative thoughts about the disease appear. Let it be inconspicuous movement for others (stroking the finger, handle of the palm);
- fully succumb to a positive sensation and carry out movement - “anchor” for several seconds;
- repeat such an exercise several times so that a pleasant memory is fixed by an “anchor”;
- if obsessive fears about the disease appear, make a movement - an “anchor”, which will automatically cause positive sensations and replace negative thoughts with them.
In the advanced stages of nosophobia, it is necessary to discard the constraint and seek help from professionals.
Obsessive thoughts - fear for loved ones

Some people are overcome by obsessive thoughts that something will happen to their relatives.
This is expressed in constant control, which prevents not only the person himself, but also to those who he is so worried about.
The main causes of fear for loved ones are usually:
- general anxiety and imagination of the personality;
- distrust of the world, formed in childhood from a feeling of insufficient safety;
- parental scenario, when, being adults, children repeat the actions of parents;
- the psycho -emotional trauma resulting from a real event that occurred with the very worrying or his acquaintances.
As in the previous case, fear for loved ones follows out of fear of death. It’s just that with this neurosis, a person worries not for himself, but for relatives (children, parents).
In order to get rid of obsessive fears for loved ones, it is necessary to work with your consciousness, applying methods for getting rid of obsessive states.
Prayer from obsessive thoughts

Reading prayer will help believers to get rid of a sense of anxiety and obsessive thoughts. She fills a person with great power and connects with spiritual powers.
You can pray:
- The Lord:
Prayer "Our Father."
- The Blessed Virgin Mary:
“The Virgin Mary, Rejoice, fertile Maria, the Lord with you; You are blessed in wives and blessed the fruit of your womb, as the Savior gave birth to our souls. ”
- Holy Trinity:
“Blessed Trinity, have mercy on us;
Lord, cleanse our sins;
Vladyko, forgive our lawlessness;
Holy, visit and heal our weaknesses, for your name "
- Angel - Guardian:
Angel of Christ, my holy guardian and the patron saint of my soul and body, forgive me, sinned by the day, and from all sly of disgusting the enemy, and in any way, the Gres is angry with my God; But pray for me for a sinful and unworthy slave, as if it is worthy of me, having had a worthy of goodness and mercy, the all -consumed trinity and the mother of my Lord Jesus Christ and all the saints. Amen
The advice of priests about the correct reading of prayers from obsessive thoughts:
- prayers speak before going to bed and whenever negative thoughts or fears overcome you;
- The Lord hears any prayer spoken with all his heart, albeit in his own words;
- you can choose a quote from the spiritual book close to you in spirit and pronounce it;
- in order to get rid of anxiety, it is useful to read the 90th psalm;
- do not hesitate, believe in the saving power of prayer words;
- it is necessary to pray constantly until you feel relief.
In addition, before addressing the Almighty, determine the nature of your obsessive thoughts to say the right words:
- with despair and unwillingness to accept what is happening - “Lord, for all your will”;
- in moments of despondency and sadness - “Thanks to God for everything!”;
- from anger at a person who has offended you - "Bless him, Lord!"
Obsessive thoughts - treatment

Unfortunately, not all people are able to fight obsessive thoughts on their own. If attempts do not bring a positive result, a person needs to contact specialists.
Specialists and psychotherapists who help the patient are engaged in getting rid of obsessive bad thoughts:
- to realize the nature of their fears;
- rethink negative experience;
- recognize true feelings and sensations;
- eliminate anxiety;
- gain a positive positive.
As a rule, the treatment of such neurosis is complex and includes several stages.
1. Psychotherapy courses in which various methods are used:
- cognitive-behavioral therapy, in which the patient is faced face to face with his obsessive fears with the installation of overcoming them;
- autogenic, based on self -hypnosis and training of relaxation;
- the method of “stopping thoughts” aimed at learning the patient to stop obsessive bad thoughts;
- treatment with hypnosis (in severe cases);
- group therapy sessions.
2. Taking medications (not always used).
The tablets from obsessive thoughts are divided into such groups:
- antidepressants who improve mood and general mental state (tolcaton, muclobemide, Imipramine, trimipramine, maPROTILIN, clomipramine, amitriptyline, citeropram, fluoxetine, cermeratin, paroxetine);
- tranquilizers that relieve anxiety, emotional tension and fear (Diazepam, Valium, chlordiazepoxide, Lorazepam, Atarax, Alprazola, Clonazepam, Queptiaapine, Elenium, Mianserin, Fevarine);
- sedative, soothing (Persen, glycine, Novopassit).
Since the long -term intake of these drugs is addictive, they are prescribed for a short time and exclusively a doctor. In severe stages, pharmacological therapy is carried out in a hospital.
Additionally, the patient is recommended folk remedies in the form of herbal infusions or tea, which have a beneficial effect on the nervous system:
- valerian;
- oregano;
- chamomile;
- mint;
- hawthorn;
- motherwort tincture;
- st. John's wort extract.
3. Auxiliary therapy aimed at improving the psycho-emotional state:
- massage;
- acupuncture;
- aromotherapy;
- relaxing baths.
The success of treatment on obsessive thoughts depends on the following factors:
- the desire of the patient himself to get rid of them;
- features of the nervous system of the patient;
- duration of the course;
- neglect of neurosis;
- the presence of other problems of a neurological nature.
Proper diagnosis and timely seeking medical assistance reduce the intensity of obsessive thinking and eliminate it completely.








Comments
a couple of years ago, there was no side of metrogils from the same problem, there were no side effects ...
I’m not a fan of peeling at all, it saves from acne of metrogil, it also smoothes it ...
Great article! ...
I take the second course of the Capsules Climafite 911. The tides went very quickly. It became calmer, irritability went away and I sleep well ...
i also noticed - it is worth nervous, everything immediately affects the face. Therefore, I try to avoid conflicts and unpleasant people. Of the creams, I like Miaflow from wrinkles - smoothes not only small wrinkles ...