Mononucleosis is a disease caused by type 4 virus. It significantly affects blood indicators and entails strong changes in the entire body. For the first time, this disease was identified and described by Dr. Filatov in the 80s of the XIX century. Mononucleosis is predominantly sick, but this disease is also found in adults, which is often in a chronic form. Without adequate treatment, mononucleosis quickly affects the lymph nodes and leaves severe complications behind. Therefore, you need to know how to distinguish this pathology from other diseases in order to prevent complications.
Content
- Mononucleosis: What is this disease?
- Mononucleosis: causes of development, transmission paths, incubation period
- Clinical manifestations of mononucleosis: specific and atypical signs
- Mononucleosis: Diagnosis of the disease in children and adults
- Than mononucleosis is dangerous: consequences and complications
- Can mononucleosis develop again?
- How to treat mononucleosis: modern approach
- Proper nutrition for mononucleosis
- Restoration of a child after mononucleosis
- Video "Children's mononucleosis - Komarovsky"
Mononucleosis: What is this disease?
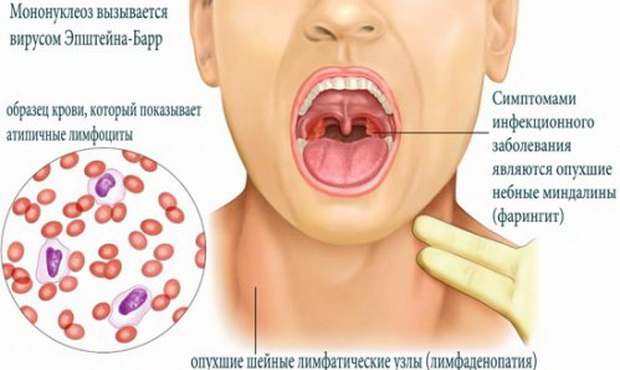
The disease of mononucleosis has an infectious nature. The disease is caused by the Epstein-Barra (VEB) special virus. It is introduced into the body with airborne droplets. If a person prontact with a virus carrier with reduced immunity, the virus begins to multiply quickly. But there are times when the body immediately produces antibodies, and the penetrated infection goes into a latent state for many years.
The virus quickly affects the lymphatic system. Infectious mononucleosis is acute, causing prolonged fever, an increase in internal organs, the development of sore throat and a critical reduction in immunity. After the cure, a person who has been ill with this disease remains a source of infection for another year.
Important! Epstein-Barr virus dies under the influence of external factors. It quickly dies when processing by any disinfectors, during boiling or after drying the surface on which it fell. The only environment where the virus survives is a living organism.
Mononucleosis: causes of development, transmission paths, incubation period
Throughout their lives, almost 90% of people will meet the VEB and most of them do not even know about it. Why, then, some people develop a complex form? The root cause of acute mononucleosis is always a failure in the work of immunity. Children under the age of 10 or in adolescence are most susceptible to this, when there is a hormonal jump: in girls this occurs at 13-16 years old, in boys-at 15-18.
So, against the background of weakened immunity, severe stress, increased loads (psychological and physical) and the absence of sufficient hygiene, infectious mononucleosis develops in children.
Interesting! Boys suffer from mononucleosis twice as often than girls.
Often the transfer of the mononucleosis virus occurs in a contact-household way: through the air or through saliva. You can catch the virus with sexual contact, through dirt on the hands, any household items. In addition, doctors assure that there are cases of infection during childbirth or during blood transfusion, plasma.
Mononucleosis is inherent in specific features, so it is quite easy to recognize the manifestation of the disease. The incubation period usually lasts at least 7-9 days, and sometimes from 10 to 50 days. As a rule, after this period, the first symptoms of the disease begin to appear. With the atypical course of mononucleosis at the end of the incubation period, catarrhal phenomena and severe weakness may occur, but soon there is an increase in specific symptoms - heat, rash, damage to the lymph nodes, liver, etc.
There are several types of mononucleosis. The primary manifestation of infection is acute mononucleosis. If the treatment was carried out inadequate, the disease can turn into a chronic form.
The body is susceptible to this virus, but subject to the normal operation of the immune system, uncomplicated mononucleosis is diagnosed. With immunodeficiency, the virus activates and develops the visceral form.
According to the severity of the symptomatic picture, mononucleosis can be typical (manifest). At the same time, the patient manifests all specific symptoms of the disease, but they can be of different severity. The opposite form of mononucleosis is subclinical. All symptoms of the disease will be absent, and the presence of the virus can only be determined after a targeted diagnosis.
In some cases, atypical mononucleosis may occur. The characteristic symptoms are not inherent in him, and instead of them the patient develops jaundice, photophobia, rash, pain after the sternum. There are also complicated and uncomplicated mononucleosis, protracted and smooth.

Clinical manifestations of mononucleosis: specific and atypical signs
Mononucleosis in adults and children manifests itself almost the same, but due to different protective properties of the body, this disease can proceed with its own characteristics. In addition, the clinical picture of the disease also depends on the very form of mononucleosis, its severity and the causes of activation.
Infectious mononucleosis: Symptoms in children
In children, the primary development of mononucleosis always occurs. The disease manifests itself as a lung SARS or passes in very severe form. The main symptoms of the reproduction of the virus, which immunity is not able to stop, are:
- Strong fever. At first, the temperature rises with mononucleosis. This is the body's reaction to the rapid lesion of the lymphoid tissue virus and toxic blood lesion with the products of its vital activity. The heat is accompanied by chills, sweating, weakness.
- Damage to the throat. Then an angina joins: there is an increase in tonsils, pain syndrome during swallowing, hyperemia, inflammation of the mucous membrane. The yellow plaque of the loose structure is noticeable, the ulceration of the mucous membrane is possible.
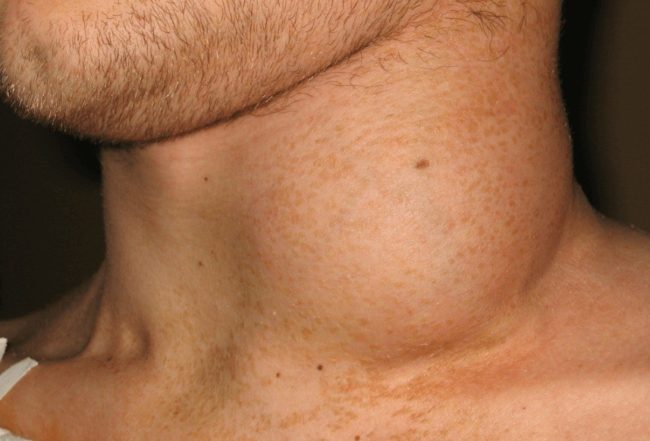
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes. Palpation of the lymph nodes on the neck, behind the ears, under the jaw confirms their increase and seal. This specific symptom indicates the introduction of VEB into lymph flow.
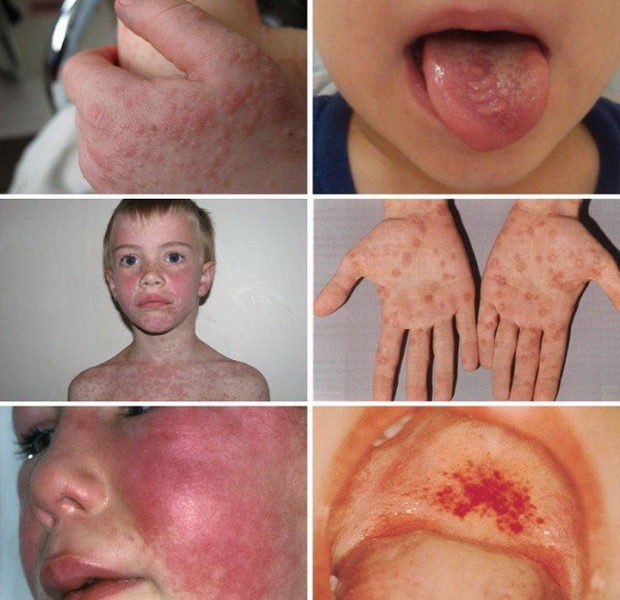
- Rashes on the skin. The rash with mononucleosis is red, in the form of single papules or merging into entire groups. It can be common in the mouth, throughout the body or in some of its areas. It does not linger for a long time and disappears after the acute symptoms of mononucleosis are subsided.
- Change of spleen and liver. The VEB is very striking in these organs: they increase in volume, the ultrasound is noticeable by the echo-signs of their dysfunction. The patient notices pain in the right hypochondrium, and yellowing can develop.
- Violation of the blood formula. A conventional blood test shows a sharp increase in monocytes and lymphocytes.
- Defeat of other internal organs. With severe immunodeficiency, VEB can lead to dysfunction of the pancreas and heart.
Mononucleosis in children in the acute phase is accompanied by fever, which lasts from 7 to 21 days. The temperature can stubbornly stay at the mark of 38-39 ° C. During this period, the child feels weakness, his muscles and head hurt, stable lymphadenoaptia (swelling of the lymph nodes) is preserved.
Note! Hepatolienic syndrome (enlargement of the liver, spleen) develops in 75% of sick children and persists for 30 days. In this case, the yellowing of the sclera, darkening of urine, dyspepsic phenomena occurs.
This is how mononucleosis looks like in the photo in children:
Symptomatic picture of mononucleosis in adults
If mononucleosis first developed in adulthood, the symptoms will be the same as in childhood. But more often in adults there is a relapse of the disease, which quietly passed into a chronic stage.
The disease can appear in different ways, but, as a rule, prodromal phenomena are leading:
- fatigue, malaise;
- decrease in performance;
- lack of appetite;
- spontaneous headaches;
- discomfort in the muscles;
- dizziness;
- soreness in the limbs at night;
- drowsiness.
Over time, a subfebrile temperature joins, which can last about a week. A significant increase in the liver may be absent. But the patient still feels soreness in the stomach, morning nausea or even vomiting.
Note! Quite often, chronic mononucleosis in adults is paired with herpes I and II. A distinctive feature of such a tandem will be relapses of herpetic rashes on the lips or genitals. Therefore, the appearance of one virus involves the diagnosis of the second.
Almost all with chronic mononucleosis, examination, has a yellow loose plaque on the tongue, larynx, tonsils. The patient often feels pain when swallowing, he can disturb the difficulty nasal breathing. A rash may also appear, which passes after 3-5 days and no longer returns.

Mononucleosis: Diagnosis of the disease in children and adults
The infectious disease specialist should be carried out by the diagnosis and treatment of mononucleosis. Only he can in the shortest possible time carry out the differentiation of the VEB from other diseases and prescribe the appropriate treatment. At the stage of diagnosis, adults and children are prescribed general clinical studies and additional specific analyzes for mononucleosis.
Nonspecific studies in children are aimed at a detailed study of the patient's peripheral blood. I would like to note right away that critical blood changes develop gradually. Therefore, the study is carried out for several days in a row after the appearance of the first symptoms.
If a child has acute mononucleosis, a blood test will be as follows:
- Medium leukocytosis.
- Sharply increased ESR.
- 10% increase in the concentration of mononuclear.
If mononucleosis is suspected, specific laboratory studies are carried out:
- Immunosporesal analysis of venous blood with the subsequent detection of the antibodies of the acute phase (IgM) or latent phase (IgG). A blood test for mononucleosis makes it possible to confirm the disease and clearly establish its form.
- PCR diagnostics for identifying DNA virus in the patient’s biomaterial (saliva, discharge, blood). Such diagnostics are very informative only in the acute phase;
- the reaction of Paul-Bunnel allows you to determine heterophilic antibodies to animal red blood cells.
Adults are carried out the same diagnosis as children. But without fail, the patient should undergo a HIV test.

Than mononucleosis is dangerous: consequences and complications
Mononucleosis can provoke complications that you have to fight for a long time. The easiest consequence is hepatitis, the most severe is fatal meningitis.
What is the danger of mononucleosis:
- It increases the risk of oncology, a poet after illness is prohibited from sunbathing for a long time.
- There is always a risk of developing meningitis and viral pneumonia, which can lead to death.
- The spleen rupture is possible, as well as the development of hepatitis.
Note! All complications are very rare and mainly associated with sustainable immunodeficiency.
Can mononucleosis develop again?
VEB is a very common virus on the planet. Just like many other viruses, for example, cytomegalovirus and herpes, it penetrates the human body in early childhood. According to statistics, almost 50% of children under the age of 5 are already VEB virus carriers. And in the group of population, which is already more than 35 years old, there are 90% of infected.
After entering the body, the VEB remains in it forever, which confirms the presence of antibodies in the blood. A person may not even know about this, since the acute form of mononucleosis is less than 20%. Most often, the disease proceeds as ordinary SARS and goes on its own, however, if the immunity works properly.
In most cases, after mononucleosis, a person remains with the developed immunity to this disease. The virus continues to "live" in the body, but antibodies do not allow it to breed. But in some cases, relapse of mononucleosis is possible. This can happen if:
- hIV-infected person. As it progresses, AIDS destroys the immune system, and all viruses become deadly for the patient, and VEB is no exception;
- a person of cancer patient or undergoes a course of chemotherapy (the disease also inhibits immunity);
- a person undergoes treatment with immunosuppressants before organs transplantation.
In a word, repeated mononucleosis is possible only against the background of clearly expressed immunodeficiency, and in all other cases the disease never returns.
How to treat mononucleosis: modern approach
Mononucleosis refers to those diseases that pass on their own. But to accelerate the recovery and prevention of complications, it is recommended to undergo treatment. It is not specific and is often carried out at home.
Infectious mononucleosis: treatment in children
In children with a mild form of mononucleosis, sparing symptomatic treatment is indicated. There are no special drugs from VEB yet, so the baby is prescribed antipyretic drugs and immunomodulators. In severe cases, when there is a risk of asphyxiation, inflammation of the lungs, meningitis, treatment of mononucleosis in children is performed in the hospital.
At home, a child can be shown:
- “Acyclovir” - antiviral tablets that destroy the structure of the virus. The course and duration of treatment is set by the doctor, but mainly the kids are prescribed after two years to prescribe 20 ml/kg of the drug for 5 days.
- “Viferon” - the drug destroys viruses and increases immunity. It is produced in the form of a gel, which is applied to an inflamed mucous membrane with a thin ball up to three times a day.
- “Paracetamol” - reduces the temperature, anesthesia, reduces inflammation in the throat. It is taken in syrup in accordance with the weight of the child.
- "Faryingosept"-prescribe 1-2 tablets per day from sore throat to relieve discomfort when swallowing.
Important! Antibiotics in mononucleosis are indicated only in the event of a secondary infection, and they do not affect the virus itself.
Antitusery drugs, rhinitis and other drugs to relieve symptoms of the disease can also be prescribed. With severe liver damage, a course of hepatoprotectors and liver fees is recommended.

Treatment of mononucleosis in adults
In adulthood, symptomatic treatment is also performed, but with the use of other drugs. Antiseptics for the oral cavity for relieving inflammation and soreness (“stoppangin”), painkillers and antipyretic drugs (“neo-Angin”, “ibuprofen”), immunostimulants (“Interferon”) are prescribed.
Probiotics for the restoration of microflora are necessarily shown. If complications have appeared in mononucleosis, antibiotics (Augmentin), antihistamines (“Loratidine”), and corticosteroids are prescribed.
Proper nutrition for mononucleosis
Since the disease affects the internal organs, the patient must adhere to a diet. For this, doctors prescribe a medical table No. 5.
It is forbidden to use:
- baking;
- fatty food;
- broths;
- sour berries;
- beans, beans;
- conservation;
- chocolate;
- shipy drinks.
They must enter the diet:
- jelly, rosehip decoction;
- rye bread;
- dairy products;
- vegetable oils;
- viscous porridge;
- vegetables;
- vegetable soups;
- boiled beef;
- sweet fruits.
Important! Involvement of the diet has a strong load on the digestive system, which can cause chronic diseases.

Restoration of a child after mononucleosis
After recovery, the baby will be weakened, so doctors recommend that you adhere to such rules:
- Hold the diet with mononucleosis, and then after recovery.
- Increase in the duration of sleep.
- Exclusion of prolonged physical exertion.
- A ban on a tan and climate change for at least a year.
- Hell for vaccinations.
Important! Excellent prevention of mononucleosis in children is full nutrition, hardening of the body and the correct daily routine.
In order to prevent the development of mononucleosis, you need to monitor the state of your immunity, lead a healthy lifestyle and adhere to personal hygiene rules. And even if you have not been able to avoid the Epstein-Barra virus, you should not be upset-timely treatment guarantees a cure for the disease without consequences.








Comments
a couple of years ago, there was no side of metrogils from the same problem, there were no side effects ...
I’m not a fan of peeling at all, it saves from acne of metrogil, it also smoothes it ...
Great article! ...
I take the second course of the Capsules Climafite 911. The tides went very quickly. It became calmer, irritability went away and I sleep well ...
i also noticed - it is worth nervous, everything immediately affects the face. Therefore, I try to avoid conflicts and unpleasant people. Of the creams, I like Miaflow from wrinkles - smoothes not only small wrinkles ...