Normally, almost all of bilirubin is excreted with feces, but a meager amount of substance enters the bloodstream. Increased bilirubin in the blood is called hyperbilirubinemia. A variety of reasons can provoke this condition: some do not cause much harm to health and do not require drug treatment, while others need urgent correction. The main symptom hyperbilirubinemia It is yellowing of the skin and/or sclera.
Content
- Bilirubin is increased - what does it mean
- Diagnosis of high bilirubin
- Increased bilirubin - norm
- Increased bilirubin - reasons
- Hemolytic (stump -shaped) jaundice as the causes of increased bilirubin
- Parenchymal (liver) jaundice as a cause of increased bilirubin
- Mechanical (subpicen) jaundice as a cause of increased bilirubin
- Physiological jaundice of newborns as the cause of increased bilirubin
- Jaundice of breastfeeding as a cause of increased bilirubin
- Nuclear jaundice as a cause of increased bilirubin
- Increased bilirubin - jaundice in a teenager
- Increased bilirubin - jaundice in pregnant women
- Increased bilirubin - what to do
- Conclusion
Next, we consider the process of bilirubin metabolism, the varieties of jaundice, the reasons for increasing bilirubin in people of different ages.
Bilirubin is increased - what does it mean
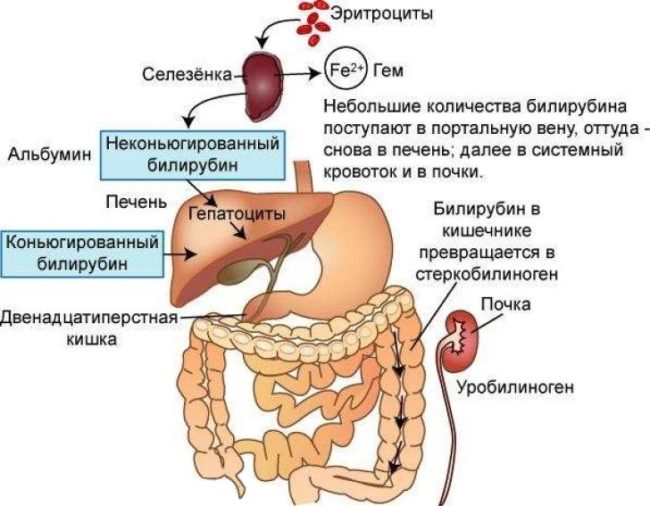
Bilirubin is a product of the decay of red blood cells, one of the components of bile, yellow-red pigment. It can be unrelated (indirect, non -manned) and connected (direct, conjugated). Hyperbilirubinemia indicates a violation at one of the stages of his metabolism.
Unrelated bilirubin is produced in the spleen as a result of the splitting of the components of red blood cells. The resulting substance is insoluble in water, fat -soluble and is toxic for cells of the body. In order to “neutralize” indirect bilirubin and remove it from the body, it is necessary to convert it into conjugated bilirubin. For this indirect bilirubin, Albumin is associated with blood protein, the latter delivers bilirubin to the liver. In addition, bilirubin in combination with albumin is not able to penetrate into the cells and pass through the filtration department in the kidneys.
The bound bilirubin is synthesized in the liver as a result of the interaction of indirect bilirubin and glucuronic acid. This substance is waterproof and non -toxic. Water-soluble bilirubin, along with bile, enters the 12-first intestine and moves along the digestive tract. In the small intestine, conjugated bilirubin is converted into a urobilinogen, 10 percent of which enters the bloodstream through the portal vein, and the remaining 90 percent is sent to the large intestine.
One half of the urobilinogen enters the bloodstream again enters the liver, and then in the 12-first intestine and moves further along the digestive tract. The second half is absorbed into the bloodstream, passes through the filtration department in the kidneys, converted into urobilin, which gives the urine yellow and excreted with urine.
In the large intestine, the urobilinogen is first converted into a stercobilinogen, and then into a stercobilin, which is excreted with feces. It is Stercobilin that gives the fecal masses brown color.
Diagnosis of high bilirubin
- The technology of quantitative determination of bilirubin fractions in newborns. Allows you to quickly and accurately determine the concentration of bilirubin in the blood. It is possible to use capillary blood.
- Urine analysis (Harrison test). The method is based on the converting of bilirubin into biliverdin and the interaction of the latter with the Fouche reagent. The presence of bilirubin in Urin is evidenced by the acquisition of green or blue liquid.
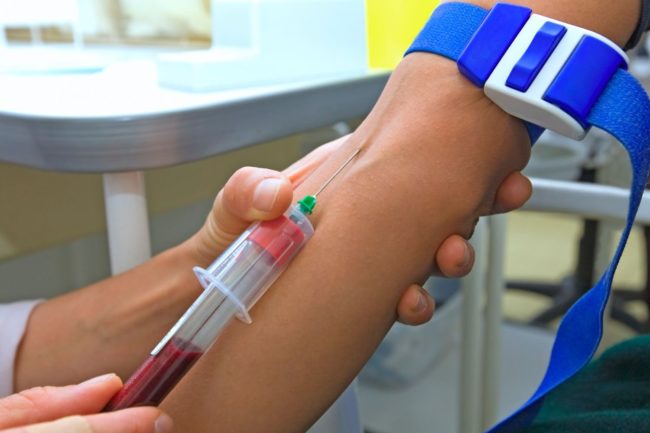
- Biochemical blood test for increased bilirubin. The amount of non -Just and conjugated bilirubin is determined, as well as their total amount - the total bilirubin. For the study, blood is taken from vein. Before delivery, you can not go in for sports, nervous, eat liquid, “heavy” food, alcoholic drinks. After the last meal, at least 4 hours should pass, it is optimal to take an analysis of on an empty stomach.
Increased bilirubin - norm
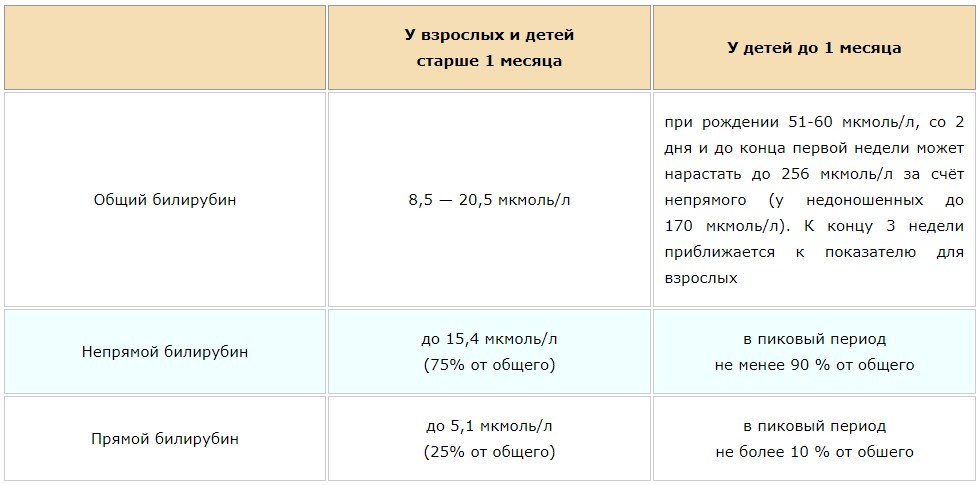
- The rate of bilirubin in the blood varies depending on the age of the patient. The floor does not matter: the indicators of high bilirubin in women and men are the same. A decreased bilirubin level is much less common. This indicates the presence of iron deficiency anemia or expressed lack of beneficial substances caused by starvation.
- Bilirubinuria is a condition in which bilirubin in the urine is increased. Normally, the urine of a healthy person contains derivatives of direct bilirubin, but their concentration is so insignificant that it is not detected using diagnostic samples.
Increased bilirubin - reasons
Hemolytic (stump -shaped) jaundice as the causes of increased bilirubin
Erythrocytes live for no more than 4 months, because their destruction and further formation of bilirubin occurs constantly. In the case of excessive destruction of red blood cells, a healthy liver does not have time to bind the non -manned bilirubin produced above the norm, and a stagnant jaundice occurs.
In the blood test, bilirubin is the total increased or normally, non -aged bilirubin is increased, conjugated - normally.
Causes:
- hemolytic anemia (both congenital and acquired);
- malaria;
- addison-Birmer disease;
- sepsis;
- rheumatic diseases;
- severe poisoning;
- helminthic invasions;
- hemolytic disease of newborns;
- taking some medications (many antibiotics, NSAIDs, aspirin, insulin and others).
Symptoms:
- rapid development of the disease;
- chills and fever are possible;
- skin color is light yellow;
- signs of anemia: pallor, weakness, decrease in hemoglobin;
- an increase in the spleen, the liver, if increased, then insignificantly.
Parenchymal (liver) jaundice as a cause of increased bilirubin
This is a violation of the metabolism of bilirubin at the stage of its transformation from unrelated into a bound. It occurs in case of damage to the liver cells: the amount of indirect bilirubin does not exceed the norm, but due to a violation of the functioning of the sick organ, it is not possible to convert the unrelated bilirubin into a bound.
Also, with this type of jaundice, the level of direct bilirubin increases, due to a violation of the formation of bile or its outflow through intrahepatic bile ducts.
In blood test, the general bilirubin is increased, indirect bilirubin is increased or normal, direct bilirubin is increased.
Causes:
- all types of hepatitis;
- ikterogemorragic leptospirosis;
- oncological liver diseases;
- cirrhosis;
- hepatotoxic poisoning;
- sepsis;
- dabina-Johnson syndrome;
- rotor syndrome;
- gilber syndrome;
- lucy-Driscoll syndrome;
- criegler-Nayar syndrome;
- pathology of the liver and taking drugs using the same enzyme systems as unrelated bilirubin (contraceptives with estradiol, paracetamol, rifadin, morphine and others), and the use of alcoholic beverages.
Symptoms:
- the disease begins gradually, it is preceded by factors that contribute to the damage to the liver, nausea and loss of appetite;
- reddish-yellow skin color. Over time, the skin can acquire a greenish tint;
- full or partial bleaching of feces;
- moderate skin itching;
- perhaps the darkening of Urina, the appearance of fever, vomiting, pain in the right hypochondrium;
- the liver is usually increased, the spleen is infrequently increased.

Mechanical (subpicen) jaundice as a cause of increased bilirubin
This disorder occurs if non-aged bilirubin is metabolized in normal quantities, transformed in the liver in conjugated bilirubin, but can be deduced due to problems with the biliary tract. The likelihood of developing a subpendry jaundice is great if bilirubin is increased in an adult or elderly. In children, this disorder is extremely rare.
In blood test, the general bilirubin is increased, indirect bilirubin is normal, bilirubin is direct increased.
Causes:
- the presence of stones, narrowing of the biliary ducts;
- cyst or pancreatic edema;
- acute pancreatitis, chronic indurate pancreatitis;
- portal biliopathy;
- mirisi syndrome;
- oncological diseases of the bile ducts, stomach, pancreatic head, large duodenal papilla, tumor or metastases in the liver.
- atresia of the biliary tract is a rare congenital disease in which the biliary tract is disturbed or completely absent in the newborn. It occurs in one of 15 thousand babies. Corrected surgically.
Symptoms:
- the disease slowly progresses with tumors, in other cases, the development is rapid;
- greenish-yellow skin color;
- bleaching feces;
- urine color of dark beer;
- strong skin itching;
- nausea, vomiting, stool disorder;
- pronounced pain in the right hypochondrium or upper abdomen;
- the gallbladder may be felt, the liver or spleen is uncharacteristic.
Physiological jaundice of newborns as the cause of increased bilirubin
It is the main cause of increased bilirubin in a newborn. In the newly born baby, the level of hemoglobin significantly exceeds such in an adult. When red blood cells decay, immature liver enzymes cannot cope with a high amount of bilirubin and the skin yellow. The absolutely normal duration of physiological jaundice is 2-3 weeks.
Physiological jaundice is from 25 to 50 newborns of 100.
Jaundice of breastfeeding as a cause of increased bilirubin
Maternal milk contains substances that inhibit the activity of the hepatic enzymes of the fetus, so the yellowness of the skin in newborn on breast feeding is observed much more often. The jaundice of breastfeeding is a common cause of increased bilirubin in a child of the first months of life. This is not a reason to refuse breastfeeding, if the rest of the child does not cause complaints and analyzes in dynamics show that the level of bilirubin is falling. With a prolonged jaundice, it is important to exclude diseases such as:
- anemia;
- atresia of the biliary tract, cholestasis;
- galactosemia;
- hemolytic disease of newborns;
- hypoteriosis;
- sepsis;
- polycythemia is true or neonatal.

Nuclear jaundice as a cause of increased bilirubin
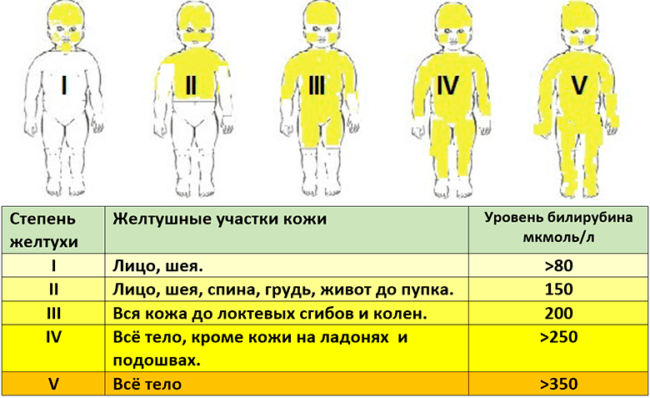
This is a severe form of jaundice of newborn, in which unanimated increased bilirubin affects the child’s body. The consequences for the central nervous system of the baby born on time cause bilirubin in an amount exceeding 324 μmol/l. For premature children, this threshold is even lower: 150-250 μmol/l.
Factors contributing to the development of nuclear jaundice:
- non -prematureness;
- hemolytic disease of newborns;
- pathological hemolysis;
- hirschprung disease;
- hemolytic anemia, spherocytosis;
- pylorostenosis;
- hemorrhages;
- enzyme;
- disorders of the endocrine system;
- intrauterine infections;
- sepsis.
Increased bilirubin - jaundice in a teenager
After the exclusion of diseases causing hyperbilirubinemia, it is reasonable to assume that bilirubin is increased in a teenager due to the congenital syndrome of Gilber. The essence of this state is a violation of the transformation of unrelated bilirubin into the required enzyme related due to the lack of the necessary. It is manifested no earlier than school age, most often it is first found in adolescents. The risk of getting Gilbert's syndrome, which increases the level of bilirubin, is several times increased in men. Gilbert’s syndrome will not be cured, but with a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition and moderate physics, it does not harm.
Symptoms:
- minor yellowness of the skin that occurs after active sports, the use of "heavy" for digestion of products, alcohol, suffered stress;
- occasionally, pain in the right hypochondrium, cramps in the abdomen;
- metal flavor in the mouth;
- loss of appetite;
- dyspeptic disorders;
- perhaps a slight increase in the liver.
Increased bilirubin - jaundice in pregnant women
Increased bilirubin in pregnant women can occur not only because of the health problems that have been acquired during conception, but also to be directly related to the fact of pregnancy. A slight increase in bilirubin in a normal woman who did not have health problems and leading a healthy lifestyle at the time of conception does not require treatment.
The reasons for jaundice caused by pathologies of pregnancy:
- early toxicosis, accompanied by strong vomiting;
- gestosis;
- intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnant women;
- shihan syndrome.

Increased bilirubin - what to do
- There are many reasons for increasing bilirubin. First you need to determine at what stage of bilirubin metabolism there was a failure and eliminate the cause/prescribe supporting therapy for the damaged organ.
- With diagnosed mechanical jaundice that provokes increased bilirubin, surgical treatment.
- Inxication, infusion therapy is used to relieve intoxication.
- To relieve intoxication in newborns with a high level of bilirubin in the blood, phototherapy is used - the effect on the skin of visible light, under the influence of which indirect bilirubin is neutralized.
- In developed countries, phenobarbital in the treatment of hyperbilirubinemia in children is not used: the harm of the drug for the central nervous system exceeds the benefits.
- For children and adults who are increased by bilirubines, diet is extremely desirable. It is important to avoid very fatty, fried, spicy foods, carbonated sweet drinks, limit the consumption of fast carbohydrates. The vegan diet is also not suitable for people with hyperbilirubinemia. In the diet, protein, slow carbohydrates must be present. You need to eat in small portions, ideally 4-5 times a day.
Conclusion
When yellowing of the skin, it is important to understand why bilirubin is increased: this determines the treatment tactics. A universal advice for people with jaundice is the observance of a healthy lifestyle, proper and fractional nutrition, and minimizing stressful situations.









Comments
a couple of years ago, there was no side of metrogils from the same problem, there were no side effects ...
I’m not a fan of peeling at all, it saves from acne of metrogil, it also smoothes it ...
Great article! ...
I take the second course of the Capsules Climafite 911. The tides went very quickly. It became calmer, irritability went away and I sleep well ...
i also noticed - it is worth nervous, everything immediately affects the face. Therefore, I try to avoid conflicts and unpleasant people. Of the creams, I like Miaflow from wrinkles - smoothes not only small wrinkles ...