Medicine is known for many causes of itching labia in women. This can be either common and, with timely seeking a doctor, gynecological diseases well amenable, and the manifestation of systemic or leaking hidden body lesions are hidden. Further, the reasons for why the labia, the tactics of the woman’s behavior with the itching of the vulva, will scratch in more detail.
Content
- The labia is itching. Vaginites (colpites) and vulvits
- The labia is itching. Kraurosis of the vulva
- The labia is itching. Bartolinite
- The labia is itching. Dermatitis
- The labia is itching. Papulosquamous diseases
- The labia is itching. Bulleous diseases
- The labia is itching. Pubic pediculosis
- The labia is itching. Scabies
- The labia in women itches. Diseases associated with metabolic disorders
- What to do if the labia is scratching
- Conclusion
The labia is itching. Vaginites (colpites) and vulvits
Vaginitis is a violation of the microflora of the vagina, accompanied by inflammation of the mucous membranes. It is a common gynecological disease: more than half of all women on the planet encounter vaginitis. In infants and children of the first years of life, the development of vaginites most often provoke an eoraillery wand, small foreign particles (sand, dust) that have fallen into the vagina, and cuts. Older children are characterized by non -specific vaginitis. Among adolescents and fertile women, specific vaginites are most often found. In the post -Climacteric period, an atrophic form of the disease develops.
Vulvit is the inflammation of the vulva. Often develops a second time: the abundant vaginal discharge characteristic of vaginitis has an irritating effect on the labia and the clitoris, which leads to the development of the inflammatory process.
If the vagina and labia are pierced at the same time, the disease is called vulvovaginitis.
Non -infectious types of vaginitis/vulvita
- Atrophic. The disease is provoked by an age -related change in the hormonal background.
- Allergic. The disease is induced by contact with the allergen.
- Mechanical. It occurs due to trauma of the genital organs (sexual intercourse with insufficient excitement, aggressive masturbation, hair removal and depilation).
Infectious types of vaginitis/vulvit
- Specific vaginitis/vulvit. The causative agent of the disease is transmitted sexually. The most common specific vaginitis: candidiasis, gonorrheal and trichomonal.
- Nonspecific vaginitis/vulvit. The causative agent of the disease refers to the conditionally pathogenic flora. It can be cocci, E. coli.
- Bacterial vaginosis. This condition is also characterized by a violation of the balance of beneficial and conditionally pathogenic representatives of microbiota, however, unlike vaginitis, there is no inflammatory process.
Sharp vaginitis/vulvit
It is characterized by pronounced symptoms. In the absence of adequate therapy over time, the symptoms are blurred, the disease goes into a chronic form.
Chronic vaginitis/vulvit
Untimely or illiterate therapy of acute vaginitis leads to the development of chronic vaginitis - disease with greased symptoms and recurrent course.
Favorable factors for the development of vaginitis/vulvit
- Infection of a number of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Hormonal changes. Age -related changes in the hormonal background, pregnancy. In a considerable percentage of expectant mothers, labia is itch during pregnancy.
- Allergic reaction.
- Deterioration of blood flow in the pelvic organs.
- Frequent acute respiratory infections.
- Lack of nutrients.
- Unprotected random sexual intercourse.
- Traumatization of mucous membranes.
- Insufficient or excessive intimate hygiene.
- Antibiotic therapy.
- Enterobiosis.
Symptoms of vaginitis/vulvita
The clinical picture will vary depending on the pathogenesis and the nature of the course of the disease. However, a number of characteristic symptoms can be distinguished:
- The labia sore and itch, discomfort intensifies during intercourse or urination.
- A burning sensation appears.
- The mucous membranes blush, swell.
- Vaginal discharge of an abnormal nature. Candidous vaginitis is characterized by curdled discharge, for trichomonal vaginitis-a grayish-green foamy discharge, for bakevaginosis-abundant discharge with the smell of non-stale fish.
Treatment of vaginitis/vulvita
For diagnosis, you need:
- smear on the flora;
- kolposcopy.
Therapy is prescribed based on the type of pathogen. Additionally, you can use special local probiotics. Healthy diet is also shown.
The purpose of the treatment of vulvit is to eliminate the root cause of the disease. To combat the disease, it is customary to use local antiseptic agents.
The labia is itching. Kraurosis of the vulva
Craurosis of the vulva is a disease in which a gradual depletion of the external genitalia occurs. Diseases are more susceptible to women after menopause. Vulva kraurosis is a precancerous state, in 2–5 out of 10 women on the background of the disease, vulva oncology develops. There is no clear picture of the pathogenesis. At the moment, the main disposable risk factor is the age -related lack of estrogens.
Symptoms of Kraurosis of Vulva
- The clitoris and labia are itching.
- The skin of the vulva dries, is thinned, depigmed, covered with cracks, and telaryctasia occurs on it.
- The entrance to the vagina is narrowing.
- Large labia lose their hair, become flat.
- The clitoris and small labia are smoothed out.
Treatment of vulva kraurosis
Usually the ailment is not cured and is chronically throughout the remaining life of a woman. However, therapy is required to prevent cancer.
Treatment is usually local and includes the use of ointment with estrogen, prednisolone ointment with anesthetic, vitamin A and injections of novocaine solution into the subcutaneous tissue of the vulva. In severe cases, vulvoectomy is required.
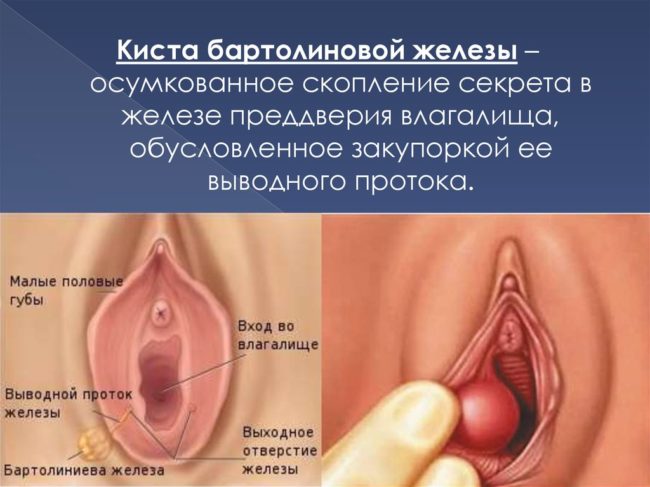
The labia is itching. Bartolinite
At the base of the large labia, bartolin glands are located - a paired organ, the main function of which is the development of a secret that moisturizes the vagina and thinning the seed fluid.
If a woman has one labia and itching, then perhaps this is a bartolinite - inflammation of the bartolin mucosa caused by the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into it: Trichomonas, gonococci, chlamydia.
Acute bartolinite
The most common is gonorrhea bartolinitis.
Symptoms of acute bartolinite:
- Large labia scratches.
- The inflamed area swells.
- The vaginal discharge has a pathological character.
- Pulsating moderate pain, which intensifies during friction.
- Harmony, weakness, increase in body temperature.
Treatment of acute bartolinite
For the treatment of bartolinite and the infection concomitant, antibiotic therapy is indicated using one of these substances: metronidazole, thinidazole, ciprofloxacin, ceftriaxone, offloxacin, azithromycin, erythromycin. The prescription of the drug is based on the results of a microscopic examination.
Chronic bartolinitis
The chronic form of the disease is usually the result of infection with trichomonas or chlamydia and illiterate or untimely therapy. It is characterized by periodic exacerbations of the course of the disease.
Symptoms of chronic bartolinite
- Atypical discharge from the vagina.
- A woman's labia is slightly itching.
- The presence of moderate pain.
Treatment of chronic bartolinite
Surgical therapy is indicated after drug treatment of concomitant inflammatory diseases.
The labia is itching. Dermatitis
Dermatitis - inflammation of the skin. Capable of affecting the area of \u200b\u200bthe external genitalia of the disease of this group are divided into:
- contact dermatitis. They occur immediately after contact with the allergen. The affected area of \u200b\u200bthe skin in size and location corresponds to the area of \u200b\u200bcontact;
- allergic dermatitis. The formation of the reaction occurs some time after contact with the stimulus. The reaction area may not correspond to the area of \u200b\u200bcontact;
- atopic dermatitis. Chronic diseases of allergic nature;
- neurodermatitis. These are eczema induced by repeated combs.
Symptoms of dermatitis
- The labia is red and itch.
- Swelling, burning.
- An increase in body temperature, a feeling of heat in the affected area.
- The emergence of blisters, bubbles.
Treatment of dermatitis
The diagnosis is established on the basis of the anamnesis and complaints of the patient, confirmed using skin allergy industry.
For productive treatment, it is necessary to eliminate contact with the stimulus, use antihistamines inside and corticosteroid ointments are locally, take sorbents and adhere to the diet. In severe cases, hospitalization is necessary.

The labia is itching. Papulosquamous diseases
Seborrhea of \u200b\u200bthe genitals
Seborrhea is a disease in which the secretion of altered sebum from the sebaceous glands is disturbed. It is dry, fat and mixed. In women, the outer surface of the genitals is affected.
The causes of the ailment are considered improper nutrition and skin care, diseases of the internal organs, nervous system, and the glands of internal secretion.
Seborrhea, symptoms
- Excessive or, conversely, insufficient secretion of skin fat. In the first case, the skin of the perineum is shiny and oily, in the second, labia ita and peel off.
- The stratum layer of the epidermis thickens.
Seborrhea treatment
The diagnosis is established on the basis of an anamnesis, symptoms, results of a biochemical blood test and analysis for hormones.
To get rid of the disease, ketoconazole, lithium succinate, selenium disulfide can be used.

Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic non -infectious disease. It affects the skin, nails, in rare cases - joints. Psoriatic plaques are most often located on the elbows, knees, chest, back, but can also affect large and small labia.
Psoriasis, symptoms
- Pink papules appear, gradually covered with white scales.
- The skin dries.
- Nodules are painful.
- The labia is itching.
Treatment of psoriasis
An effective treatment complex for combating sexual psoriasis includes:
- corticosteroid ointments;
- local use products with vitamin D;
- tar ointments;
- herbal, salt, turpentine baths.
- the irradiation of the affected areas with an ultraviolet light is strictly according to the doctor’s testimony.

Red flat lichen
The exact causes of this disease are unknown, the autoimmune nature of the disease is assumed. According to statistics, at risk are women who have stomach diseases, diabetes.
Flat lichen affects the skin of the legs, chest, abdomen, nails, mucous membranes.
Flat lichen, symptoms
- Mucous vagina, small labia, blush.
- The bleeding of the mucous membrane of the vagina.
- Whitish stripes on the mucous membranes appear.
- Small labia, large labia.
Treatment of flat lichen
Drug therapy is required during periods of relapse and includes corticosteroids in the form of injections, ointments and antihistamines. In a severe course of the disease, treatment with ultraviolet light may be prescribed.
The labia is itching. Bulleous diseases
Pemfigus (bubble)
Bubbles are an autoimmune disease that affects the skin and mucous membranes. It is ordinary, leaf -shaped, seborrheic and vegetative, it is the latter who usually affects Vulva.
The disease is dangerous in that it can lead to sepsis, heart disease.
Bubbles, symptoms
- Filled with liquid pimples on the labia that itch. After opening in their place, erosion covered with gray raid.
- In the absence of adequate therapy at the bottom of erosion, fetid and easily bleeding growths are formed up to 3 centimeters high. In the stage of regression, damaged places are dry, covered with crust and cracks, which causes severe pain.
Treatment of bubbles
The diagnosis is based on the clinical picture, the results of the Nikolsky phenomenon, cytological, histological, immunofluorescent studies.
For treatment, corticosteroids are used. In severe course, cytostatics are also prescribed. If necessary, plasmapheresis, hemodialysis, and hemosorption can be performed.
Haley-Heili disease
The ailment affects the skin, mainly in the folds. Often manifests itself in people aged about 40 years. Among the factors giving impetus to the disease, friction, heat, infections are indicated.
Haley-Haley disease, symptoms
- The appearance of bubbles, erythematous plaques with crusts.
- Itching.
- Burning.
Haley-Haley disease treatment
To confirm the diagnosis, tissue biopsy is required.
Therapy includes wet compresses, the use of corticosteroids and antibiotics. Nowadays, glycopyrrolate is also actively used to control sweating.
Multicomorphic erythema
Multicomorphic erythema is an acute allergic disease, in which a specific rash appears on the mucous membranes and skin. The most common among people of young and middle ages. The exact causes of occurrence are currently not established, but there is a correlation between the presence of chronic diseases and the risk of a multi -morphic erythema.
Symptoms of multi -interfesse erythema
- Mialgia and atralgia.
- Improving body temperature.
- Weakness.
- Growing flat reddish pink papules with clearly defined edges.
- Itching.
- Burning.
Treatment of multicomorphic erythema
The diagnosis is established on the basis of an anamnesis, symptoms and dermatological examination. The treatment is aimed at the prevention of relapses and the relief of symptoms during exacerbation is carried out by a gynecologist and a dermatologist. The use of antihistamines, the local use of corticosteroid ointments or antibiotics is shown.
The labia is itching. Pubic pediculosis
The causative agent of the disease is a pubic lice - an insect that feeds on blood. The pubic louse lives and lays eggs, mainly on the hair in the inguinal zone, but it can migrate to other parts of the body covered with hairline. Infection is carried out by sex and domestic way.
Pubic pediculosis, symptoms
- Itching, the labia is very itchy, pubis at night.
- An allergic rash is possible in places of bites.
- Detection of nits on the hair.
Treatment of pubic pediculosis
The diagnosis is based on the symptoms and detection of insect eggs. To get rid of pubic lice, local -acting drugs are used. Treatment should undergo both sexual partners. A change in linen and its subsequent boiling is also necessary.

The labia is itching. Scabies
The disease is extremely contagious. The causative agent is a scabies, which is active in the dark, is able to infiltrate the skin 15 minutes after contact.
With primary infection until the signs of the disease appear, it can take up to 4 weeks, with repeatedly, the symptoms can occur after a day after a day.
Scabies, symptoms
- The labia itchs strongly in the dark.
- The appearance of an erythematous papuloveycular rash.
- The presence of scabies.
School treatment
The diagnosis is based on symptoms and laboratory tests.
Scabicides are used to destroy ticks. The treatment regimen is painted with a doctor, processing is performed on the second half of the day, at the end of the course, underwear and bedding are replaced. Children under 3 years of age are applied to the whole body, adults - to the whole body, with the exception of the skin of the face and the scalp. Therapy must pass all contact persons. During the course of treatment, it is not recommended to take a bath or shower.

The labia in women itches. Diseases associated with metabolic disorders
If the labia is itchy, then the cause of this should not be the presence of an objective disease. In the absence of such, itching may be due to the presence of one or more of the following diseases:
- Diabetes.
- Violation of the metabolithic functions of the liver or kidneys.
- Depression.
- Anxiety.
- Iron deficiency anemia.
- Hidden flowing states. For example: systemic fungal damage to the body.
- Supersensitivity to certain drugs.
What to do if the labia is scratching
First, it is worth excluding possible non -infectious causes of itching:
- wearing panties from artificial materials;
- wearing a tight fitting pelvis;
- insufficient or excessive intimate hygiene. Carrying up vulva needs to be carried out daily, for this only warm water is used. High -quality soap that does not contain dyes, extracts of herbs is allowed every 1-2 days;
- the use of hygienic tampons, menstrual bowls, daily gaskets;
- if the labia is itching after sex, then it is necessary to exclude ejaculate entering the genitals (allergies can also develop on men's seed) and, if necessary, additionally use a hypoallergenic lubricant;
- using allergenic contraceptives: candles, spermicides. If, after relations in the condom, the labia is itching inside, then it is worth trying hypoallergenic condoms from polyurethane.
If the above measures did not bring relief, then you need to undergo an examination in the clinic.
Conclusion
There is no unequivocal answer to the question “The labia is itching than to treat”. Itching labia can be caused by venereological, gynecological, dermatological diseases and conditions in which metabolic processes are impaired in the body. Self -medication is unacceptable, an accurate diagnosis and treatment regimen should be prescribed by a doctor.








Comments
a couple of years ago, there was no side of metrogils from the same problem, there were no side effects ...
I’m not a fan of peeling at all, it saves from acne of metrogil, it also smoothes it ...
Great article! ...
I take the second course of the Capsules Climafite 911. The tides went very quickly. It became calmer, irritability went away and I sleep well ...
i also noticed - it is worth nervous, everything immediately affects the face. Therefore, I try to avoid conflicts and unpleasant people. Of the creams, I like Miaflow from wrinkles - smoothes not only small wrinkles ...