The vector of attention of modern society today is aimed at an active lifestyle and proper nutrition, but many of us, unfortunately, have not mastered the culture of drinking drinking water. Due to the water deficiency, the human body experiences a state of dehydration, in other words, is dehydrated. This is not a disease, but a very serious pathology, which in advanced cases threatens human life. You can encounter dehydration at any age, so it will not be superfluous to find out about a dangerous disorder maximum information: why it develops, how to recognize and how to cure.
Content
- Forms and stages of dehydration
- The main symptoms of dehydration of the body
- Why develop dehydration in adults and children
- What is the dehydration of the body
- Risk groups when dehydration
- Treatment of dehydration of the body
- Treatment of more serious dehydration of the body at home
- What to drink when dehydration
- Dehydration: when you need medical care
- The consequences of dehydration of the body
- How to prevent dehydration
Forms and stages of dehydration
Lack of liquid develops when a person consumes much less water than produces his body along with later, urine, etc. The development of dehydration is customary to divide into several stages:
- mild degree - is lost up to 3% of the liquid. A fairly common phenomenon that does not threaten life;
- the average degree - the body loses up to 6% of the water. In this case, there is a slight danger to human health;
- a severe degree - fluid in the body becomes 9% less. A large risk to the patient’s health and life develops on this basis;
- critical degree - the body leaves more than 10% of water. Inner irreversible processes occur, which most often lead to death.
This classification is relevant for people of any age, including children.
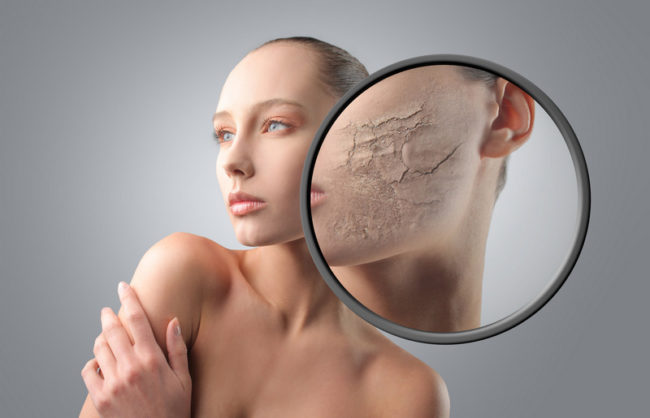

The acute and chronic form of pathology is also distinguished. In the case of acute dehydration, the patient is very losing weight in a matter of days. The state of dehydration develops so quickly that the transition from the first stage to the latter is almost impossible to track. If you do not help in such a situation in time, a person dies.
In the chronic process of dehydration of the body, a person is subjected to mild and medium degree of dehydration. Neutralizing the signs of pathology is quite simple, but the general condition of the patient does not change due to external and internal factors.
Since dehydration is evidenced by a number of indicators, the patient's condition is evaluated comprehensively, taking into account the factors that caused the development of dehydration.
The main symptoms of dehydration of the body
The clinical picture of dehydration is very diverse. We note the most indicative features:
- strong thirst, "sand" in the mouth and throat;
- dry mucous membranes and skin, sticky and swollen tongue;
- dizziness with loss of consciousness;
- gradually growing headaches;
- constant fatigue, drowsiness;
- slow concentration of attention, impaired coordination of movements, distraction;
- suppressed mood, indifference, unreasonable anxiety, susceptibility to panic attacks;
- increased viscosity and density of saliva;
- disorder of normal urination (change in frequency, volume and color of urine). In severe cases - anuria;
- poor appetite, in the absence of treatment - its complete loss;
- marble or bluish skin;
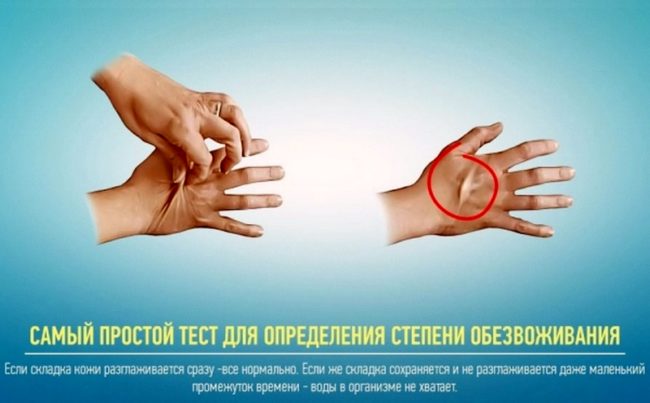
- the absence of a well -groomed look in the skin - the skin is losing elasticity, peeling strongly, covered with pronounced wrinkles. If you squeeze the skin fold between the fingers, and then release, the fold is smoothed only after a while;
- muscle pain, muscle cramps, tremor of the head and limbs, articular pain, pain in the internal organs;
- irregular chair or its complete absence;
- low body temperature and low arterial pressure, a feeling of numbness in the lower and upper extremities, a rapid pulse, a rapid heavy palping;
- sympy, quiet voice;
- dyspnea;
- sharp ejacons to the face.
The severe form of dehydration accompanies additional symptoms:
- thrustful eyes;
- sticky film on the skin;
- shadows under the eyes;
- confusion, delusional state;
- disorder of the functions of the lacrimal glands;
- slow down, superficial breathing.

The chronic form of pathology also has pronounced symptoms:
- constant thirst, which is very difficult to satisfy;
- frequent headaches passing into migraine;
- heartburn, digestive disorder;
- muscle pain in the arms, legs, joints, backs.

The above symptoms of dehydration of the body are found in adults and children. Age does not affect the symptoms of disorder.
In infants, individual signs of dehydration of the body, characteristic of this age are noted:
- lack of urination for more than 7 hours;
- dark urine with a sharp and strong smell;
- a furtive fontanel;
- lethargy and constant whims;
- baseless anxiety, crying without tears;
- periodically occurring vomiting and liquid stool.

Why develop dehydration in adults and children
There are a lot of factors due to which this or that degree of dehydration appears. Almost all reasons cause a deficiency of fluid in the body at any age.
The root causes of dehydration:
- insufficient flow of drinking water into the body during the day;
- poisoning, which is accompanied by unbridled vomiting and prolonged diarrhea;
- enhanced work of the sweat glands;
- thermal, sunny blow, feverish condition with high body temperature;
- excessive physical activity in the heat or in a closed room without access of fresh air, long and heavy sports;
- abuse of coffee and alcoholic beverages;
- bad habits in the form of smoking cigarettes and drug use;
- taking certain drugs: diuretics, laxatives, antidepressants;
- starvation, violation of food behavior (for example, anorexia);
- diabetes mellitus;
- severe diseases of infectious etiology;
- severe injuries and injuries that are accompanied by massive bleeding;
- mental disorders;
- violation of metabolism;
- high degree of exposure to stress.

In infants, fluid lack of fluid in the body develops if, during the period of completeness input, they do not receive water in sufficient volume. In addition, the culprit of a dangerous disorder in children of the first year of life often becomes completely not formed by the heat transfer mechanism in the body.
What is the dehydration of the body
- hyposmolar dehydration. The body loses a large number of electrolytes. This occurs as a result of injury, wound or adrenal disease;
- izoosmolar dehydration. Is a consequence of a severe infectious disease, also develops on the basis of serious blood loss;
- hyperosmolar dehydration. It is observed in the body during vomiting, prolonged diarrhea, taking diuretic drugs, renal diseases.
Risk groups when dehydration
It is probably impossible to die from a liquid deficiency in a metropolis, however, a risk to life associated with dehydration always exists. More than the rest of the danger are affected by infants and children who have not reached adolescence.
Being in a state of acute form of dehydration, a person can die in a matter of hours, but the chronic form of pathology without proper treatment leads to death. Without water, an adult dies for 10 days, and the child - after 4 - 5 days.
The risk group consists of:
- newborns and children under 10 years old;
- the population of the southern countries and the inhabitants of the mountains;
- athletes, fans of long tourist expeditions;
- people of advanced age, in whom metabolic processes in the body slow down over time;
- people of all ages suffering from kidney diseases, liver and endocrine system;
- people of all ages with congenital and acquired mental illness, various forms of depressive state;
- people engaged in work outside the room, as well as in adverse climatic conditions.

Treatment of dehydration of the body
Dehydration of the body cannot be underestimated, especially since at the initial stage of the pathological process, a person can correct his condition on his own. The faster the disorder is eliminated, the faster and easier the body will restore its natural functions.
What to do with mild dehydration of the body? It is enough to make up for the loss of liquid by using filtered water or mineral water with a certain percentage of salts. To normalize well -being faster, you need to be in a clean room with a constant flow of fresh air.
The correct drinking regime provides for a person to drink in small sips of 1.5 - 2 liters of water per day. In this case, you need to forget about teas and caffein -containing drinks for some time. But natural, diluted or concentrated juices, fruit drinks and unsweetened compotes will be very useful.

While the symptoms of dehydration are preserved, you need to adhere to a simple diet. This is what food will help bring health to normal:
- not greeted meat broths;
- vegetable soups;
- products with a high potassium and sodium content: bananas, raisins, tomatoes, oranges, lemons, potatoes, green vegetables, nuts.
With hot weather conditions and high physical activity, an adult is recommended to drink at least 1 liter of water per hour. If you are responsible for the baby or older baby, approach the child’s drinking regime with all responsibility. When it is very hot outside, children need to drink an approximate 150 ml of water in 30 minutes. Older people are also advised to drink more water. On the basis of acute colds and infectious diseases, high body temperature, the volume of daily fluid is best increased by half (up to 3 - 4 l).

After eliminating the state of dehydration, help the body recover. The internal water-salt balance will return to normal faster if you do not use the following products:
- alcoholic drinks (smoking also need to be abandoned);
- sweet "soda";
- medicines and herbal fees with a diuretic or laxative effect.
Treatment of more serious dehydration of the body at home
In conditions of more pronounced dehydration of the body, plentiful drink should be supplemented with the following recommendations:
- ventilate the room in which the patient is located, ensure the movement of air with a fan or air conditioner;
- lay a person and wipe his body with a sponge moistened with water at room temperature (but in no case with cold or ice water);
- put the patient with a cool compress on the forehead.
During medium -sized water, water is drunk with small sips through a straw. The baby is soldered with a syringe without a needle.

What to drink when dehydration
There are special tools to accelerate the restoration of water-salt balance in the body. They can be bought at a pharmacy or make them yourself.
Here are a pair of recipes for therapeutic solutions that are simply prepared at home:
- Take 1 liter of boiled warm water and dissolve there a teaspoon of salt, 3 tablespoons of sugar and half a teaspoon of baking soda. Mix the ingredients well. All! The medicine is ready - it must be drunk in small sips during the day.
- Take orange juice in a volume of 200 ml and pour half a teaspoon of salt and a teaspoon of baking soda there. Lastly, add 800 ml of boiled slightly warm water to orange juice. Let the patient drink a therapeutic solution as thirst.

Let us recall the drugs effective in dehydration.
Regidron when dehydration of the body
In order to prevent the development of dehydration of the body with diarrhea or indomitable vomiting, they drink 200 ml of a medicinal solution. If the signs of dehydration are already evident, the treatment regimen is different: the product is taken at the rate of 50 - 100 ml of the drug per 1 kg of body weight in the first 4 - 10 hours of dehydration. When the patient becomes easier, he is transferred to the prophylactic volume of the regron.

If the patient cannot drink a salt solution due to vomiting, after the next attack, the medicine begins to drink 1-2 tsp. Every 5 - 10 minutes. It is impossible to mix additional ingredients to the finished solution of regions. Parallel use of other drinks is allowed, but without sugar. The drug is intended for the treatment of adults, children, infants and pregnant women.
Toural when dehydration of the body
To prepare the solution, dissolve 2 tablets of the drug in 100 ml of hot water, and then cool the liquid to room temperature. The dosage is determined by the age of the patient, but on average it is recommended to drink 90 - 130 ml per 1 kg of body weight. The volume of the product is reduced as they recover.
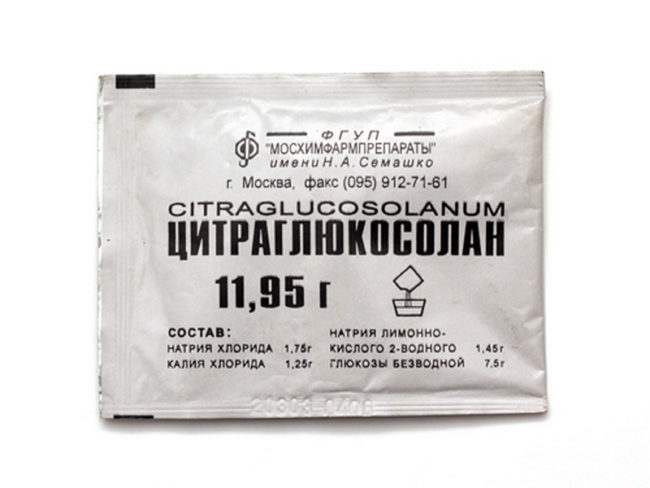
Citraglucosolan when dehydration
The composition of the drug contains glucose and various salts. The medicine is effective in dehydration, which appeared against the background of severe diarrhea and severe vomiting. The powder of one bag must be diluted in warm boiled water. Citraglucosolan is available in bags of different masses:
- the contents of the package weighing 2.39 g are diluted in 100 ml of water;
- 11.95 g - 0.5 l of water;
- 23.9 g - 1 liter of water.
With a mild form of disorder, the patient is offered 2.5 - 3 liters of a solution of citralcosolan, and in serious cases, it is allowed to increase the volume of a liquid drug to 5 l.
With severe dehydration, treatment is prescribed already in the hospital. The patient is placed droppers with infusion solutions, when exposed to which the normal volume of water and electrolytic substances in the body is restored.
Dehydration: when you need medical care
Urgent intervention of a doctor in the situation is necessary if:
- Symptoms of dehydration manifested themselves in the baby, a child who is not yet 10 years old, or an advanced person.
- In the patient's condition, the following alarming changes are observed:
- diarrhea for more than 2 days;
- headaches, fainting;
- nausea and vomiting lasting more than 12 hours;
- lack of urination for more than 12 hours;
- feverish condition with high body temperature;
- heavy breathing;
- painful pain in the abdomen;
- convulsions.
The consequences of dehydration of the body
Acute and chronic dehydration can equally undermine the patient's health. These are the consequences usually leads to a lack of fluid in the body:
- development of irreversible mental deviations;
- nervous and emotional exhaustion;
- high risk of developing myocardial infarction on the basis of depletion of heart muscles;
- the risk of thrombosis;
- hypoxia in children;
- high probability of violation of the activity of the kidneys, adrenal glands, bladder and digestive organs;
- decrease in the protective forces of the body;
- severe pain in the head and internal organs;
- pathological changes in the bones and joints;
- violation of muscle tone;
- decrease in mental activity;
- constant fatigue;
- regular boards of blood pressure.

How to prevent dehydration
Finally, we share with you effective tips from specialists who will help to avoid dehydration of the body:
- beware to work physically in hot weather;
- try not to be in the midday heat in the open air - it is better to relax in a shaken, cool place;
- always have water with you;
- control the use of alcoholic beverages;
- limit yourself in the consumption of sweet and sugar;
- give preference to clothes from high -quality breathable fabric.
Following these simple rules, you will not be able to experience the harmful effects of dehydration on yourself. Be healthy!








Comments
a couple of years ago, there was no side of metrogils from the same problem, there were no side effects ...
I’m not a fan of peeling at all, it saves from acne of metrogil, it also smoothes it ...
Great article! ...
I take the second course of the Capsules Climafite 911. The tides went very quickly. It became calmer, irritability went away and I sleep well ...
i also noticed - it is worth nervous, everything immediately affects the face. Therefore, I try to avoid conflicts and unpleasant people. Of the creams, I like Miaflow from wrinkles - smoothes not only small wrinkles ...