Breaking through the brain is one of the most common traumatic brain injuries. Despite the fact that it is the most “light” among these injuries, in any case, it is impossible to underestimate the concussion. You can get such an injury anywhere - at home, on the street, at work, in a store, etc. A concussion can occur not only with a direct impact of the head on a solid surface, but also when falling into the buttocks, for example. It is for this reason that fractures, bruises and other body damage are frequent "satellites" of the concussion. In this article, we will figure out how to recognize a concussion in an adult or child, in what situation you can not hesitate to see a doctor, what to do with a concussion, what to drink with concussion, which drugs treat concussion and find out whether it is necessary at all Heal it.
Content
- Brack of the brain in an adult or child - what is it
- How to determine a concussion
- A concussion of the brain - where and when can be a danger
- Brain concussion - symptoms
- Brand of the brain in the child
- The degree of concussion
- First aid for concussion
- Diagnosis of the concussion of the brain
- How to treat a concussion in an adult
- The consequences of a concussion
- Complications of the concussion of the brain
Brack of the brain in an adult or child - what is it
Breaking through the brain's concussion is a common craniocre trauma, characterized by “shaking” the soft substance (brain) inside the cranial box. This usually happens when the head falls and hit on a firm surface. The severity of the symptoms of a concussion of the brain will depend depending on what power was a blow. The human brain is an incredibly complex and amazing organ. Scientists did not fully understand what exactly happens in the brain at the time of a concussion. The following processes can occur in the brain at the time of injury:
- loss of communication between neurons;
- short-term spasm of blood vessels, which is why the diet of the brain occurs;
- temporary loss or violation of the connection between the cerebral cortex and other structures of the brain;
- increased pressure inside the cranial box;
- temporary change in the direction of the movement of cerebrospinal fluid;
- there is a slight displacement of layers of brain tissue;
- temporary changes in the brain at the molecular level.
Thus, the main distinguishing feature of such a traumatic brain injury as a concussion, is that all changes in the brain at the time of injury are reversible and no morphological changes in any parts of the brain occur. If such changes are nevertheless confirmed, then this is no longer a concussion, but another, more serious, traumatic brain injury.
How to determine a concussion
Why does an ordinary person know how a concussion is determined? After all, only doctors should deal with this issue. But you must admit that the knowledge of some signs of a concussion will help not to miss this injury. So, imagine that the person fell and hit his head. You can suspect a concussion from him on the following signs:
- after hitting his head, a man lost consciousness. Depending on the severity of the injury, loss of consciousness can last from a couple of seconds to a couple of minutes. In difficult situations, a person can fall into a coma;
- after hitting his head, a person does not recognize people familiar to him, cannot name his name, cannot recall some events that took place before the fall. Doctors determine the severity of the concussion by a segment of the time, which "fell" from human memory. The more events he cannot recall, the stronger the changes in the brain were;
- after impacting his head, it is difficult for a person to concentrate his eyes, he feels pain when moving eyeballs;
- after the person’s head is struck, it tears or sick;
- after hitting his head, a person feels pain in the occipital part of the head for a long time;
- after a head hit a person for a long time, he feels weakness, dizziness, has sleep disorders;
- after impact, blood pressure may increase or decrease, the pulse can also be both increased or low.
If at least one of the signs listed above is present in a person after falling, hitting his head, then with a high degree of probability he may have a concussion. It is not worth pulling a qualified doctor with an appeal to a qualified doctor.

A concussion of the brain - where and when the danger can wait
You can get a concussion more often than you think. We are in wait for the dangers at every step. Light traumatic brain injury can easily be “earned” in the following situations:
- under the influence of alcohol. It is no secret that people “under the degree” often cannot maintain balance, fall, and inflict injuries themselves. Breaking through the brain is one of the most common injuries in such situations, the diagnosis of which is significantly complicated if a person is drunk. You can easily confuse the symptoms of a concussion with the "normal" behavior of a drunk person;
- during sports. In order to get a concussion, it is not necessary to engage in extreme sports. You can just get a ball on the head while playing volleyball;
- during the ice. In winter, as a rule, the number of patients with various head injuries, including concussions of the brain, increases significantly. Recall that the brain can “shake” the brain without a direct blow to your head. A strong fall on the buttocks can also provoke the occurrence of a light traumatic brain injury;
- while driving by car or other transport. You can get a concussion with a sharp braking of the vehicle. Children who, contrary to all safety rules are not fastened with a seat belt, are not sitting in a car seat, etc. are especially susceptible to such injury.
As you already understood, you can get a concussion very easily. It is very important to explain to the children that any blows to the head during games are simply unacceptable.

Brain concussion - symptoms
In order to provide assistance to the victim in time, it is very important to know the most common symptoms with concussion. Depending on the state of health, on individual characteristics, on the strength of the blow, these symptoms can manifest itself to varying degrees or not manifest at all. So, the symptoms of the concussion are:
- nausea or vomiting are the most frequent "satellites" of concussion;
- confusion;
- violation of coordination;
- a feeling of significant discomfort from bright light or loud sound;
- "Failures" in memory;
- loss of consciousness for a while. If the loss of consciousness after a head strike lasts more than 6 hours, then most likely there were any irreversible processes in the brain, a coma may occur;
- pain after a concussion when eye movements;
- expanded or narrowed pupils, a different size of the pupils of both eyes;
- drowsiness;
- excessive activity and energy;
- convulsions;
- speech disorders;
- increase or decrease in blood pressure;
- pale skin or their redness.
It is worth noting that the temperature with concussion does not increase or increases slightly.
Brand of the brain in the child
Signs of concussion in the child
Among the CCMT, a concussion in children is diagnosed in more than 90% of cases. What is it connected with? You can distinguish a number of reasons why children get a concussion:
- poor coordination in children of nursery and preschool age. Children are excessively active, very curious and a completely unfamiliar sense of fear. The usual fall of the baby in the sandbox can turn into a slight form of traumatic brain injury;
- features of the structure of the body in childhood. The head of the children “outweighs” them when falling, pulls down, and children still do not know how to take a safe position during the fall. This is another important cause of injuries in childhood;
- syndrome of "shaken child." Children can get a light traumatic brain injury during intense swing on their hands, tossing into the air, which only seems harmless and cheerful pampering;
- parental mistakes. Unfortunately, a huge number of brain concussions in children might not have, if adults did not leave the kids unattended, they did not leave "for a minute." Children often fall from the bed, from a changing table, fall out of strollers, from cribs, etc.
As for the clinical picture of a concussion in childhood, it is not very different from the symptoms of similar injury in adults. The main difference is the difficulty in diagnosis. Children of school and preschool ages often do not report their falls, and to understand that the baby is bad at all very problematic. Consider the main symptoms of the concussion of the brain in children:
- sleep disturbances;
- capriciousness and tearfulness;
- regurgitation in babies, nausea, vomiting;
- the pallor of the skin;
- loss of consciousness for a short time;
- temporary blindness, the cause of which scientists have not yet established;
- sweating;
- loss of appetite;
- nervousness.
Another very important feature of the concussion in children is that any symptoms can immediately be absent after a head hit or after a strong fall, and appear after a while.
Treatment of brain concussion in a child
How to help with a concussion in a child? If the baby received a bruise of the head, fell, then you need to call an ambulance to evaluate his condition in the shortest possible time. Before the doctor’s arrival, you need to calm the child, put him on the side, and by any means try to limit his motor activity. If the child has a wound on his head, then you need to stop the blood and apply a sterile bandage. It is also a very important point that a child cannot be allowed to fall asleep within 2-3 hours after a bruise of a head or fall. If the child is still hospitalized in the hospital with a diagnosis of a concussion, then it will be treated with the following drugs (in light cases, drug treatment may not be needed):
- diuretics;
- drugs to maintain potassium;
- antihistamines;
- sedatives;
- painkillers;
- nootropic drugs.
After discharge home, the child will be prescribed a course of treatment that will need to be followed. Typically advised to take vitamins and nootropic drugs at home if necessary.
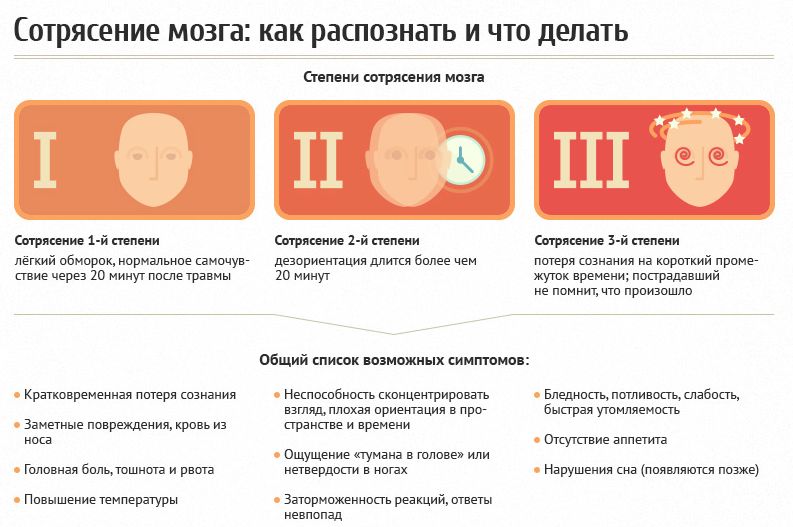
The degree of concussion
Depending on the severity of the concussion, 3 degrees of this traumatic brain injury are distinguished:
- a mild degree of concussion. This degree is characterized by a short -term loss of consciousness no more than 5 minutes. A person comes to normal in 20 minutes. If with a light concussion there was no loss of consciousness, then people do not even pay attention to this;
- the average degree of concussion. This degree is characterized by the loss of consciousness for no more than 15 minutes. After fainting, the victim retains disorientation in space, a violation of some functions. An appeal to the doctor of the victim with an average degree of concussion is mandatory;
- a severe degree of concussion. This degree is characterized by a loss of consciousness, which lasts more than 20 minutes. Disorientation in space, amnesia, disturbed motor skills and other symptoms of concussion persist for a long time after a bruise of the head or fall. At this stage there may be a coma. An appeal to a doctor with a severe degree of concussion is mandatory.
Of course, only a doctor is engaged in the definition of one degree of concussion of the brain. The severity of this traumatic brain injury depends on the duration of the loss of consciousness, on the presence or absence of convulsions, on the size of the period of time that “fell” from human memory.
First aid for concussion
What first aid can you independently provide a victim with a concussion? Consider an approximate algorithm of your actions:
- if a person hit his head and lost consciousness, then you cannot know for sure whether this is a concussion or a heavier traumatic brain injury. The first thing to do is call an ambulance team;
- put a person on the right side, bending your left leg and left hand. This is necessary so that the victim in case of vomiting does not choke in the vomit;
- ung in the collar, remove the tie, provide free access of fresh air;
- if there are bleeding wounds on the head or other parts of the body, then the blood must be stopped and sterile bandage;
- attach the ice to the places of bruises;
- follow the pulse and pressure of the victim, if there is such an opportunity;
- do not let the victim sleep before the ambulance arrived;
- remove the sources of loud sound, bright light, as this can bring significant discomfort to a person with a concussion;
- if you stop breathing before the ambulance arrived, then immediately begin to carry out cardiac-and-bearing resuscitation.
Diagnosis of the concussion of the brain
An experienced doctor can determine the concussion of the brain by several symptoms. In complex and ambiguous situations, the doctor will prescribe a number of studies to confirm or exclude more severe traumatic brain injuries. You can recognize a concussion after examining the victim and after his answers to some questions:
- is there a sense of tension in the occipital part of the head;
- whether the injured equilibrium in the pose of Romberg (legs together, hands are raised parallel to the floor, the eyes are closed);
- is the victim to focus without problems, monitor the subject;
- is the asymmetry of some reflexes present;
- whether the pupils of the victim are in the normal state;
- is there no pain, discomfort when eye movements.
A concussion of the brain in infants, children of preschool and primary school ages can confirm the presence of nausea, vomiting, rapid or slow pulse, pallor, drowsiness or excessive activity, frequent regulations, impaired sleep and tearfulness. If the doctor doubts the correctness of the diagnosis, the following studies may be prescribed:
- head X -ray;
- with a concussion of the brain or CT - the most commonly used examination methods;
- Ultrasound of the brain;
- the study of the eye bottom;
- spinal puncture;
- EEG;
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the head.
How to treat a concussion in an adult
Treatment of brain concussion at home
If you decide to treat a concussion of the brain, then in any case, the doctor should give you permission to do this. This is usually allowed if the degree of concussion is light, and the well -being of the victim after a bruise or fall improves every day, the symptoms disappear. The doctor can give the following recommendations for the treatment of a concussion of the brain at home:
- compliance with bed rest;
- emotional peace;
- restriction of physical activity;
- it is not recommended to listen to music through headphones, watch TV, play video games;
- nutrition should be light and nutritious with limited salt content;
- you can drink herbal teas, soothing herbal fees;
- if headaches periodically occur, then taking analgesic drugs is possible.
But do not forget that even a slight concussion is a traumatic brain injury that can remind itself after months or even years. Be sure to show yourself to the doctor to select the optimal course of treatment.
Treatment of brain concussion in the hospital
If the doctor considers it necessary to hospitalize the victim with a concussion, then it is impossible to refuse in any case. The main goal of treating a concussion in an adult in a hospital compartment is to observe and relieve symptoms of injury. In the hospital, the following types of drugs with concussion can be prescribed:
- anesthetic drugs (Ketorol, Baralgin, Analgin, Pentallgin). After a concussion of the patient, rather severe headaches, migraine can be disturbed. Analgesic drugs are designed to alleviate the condition of the patient;

- sedatives (Valerian, motherwort, Corvalol). In the treatment of concussion, it is very important to observe bed rest, you need to limit physical activity, be in a calm environment;

- tranquilizers (nosepam, phenosepam). This group of drugs with a concussion is required if, after an injury, a person is too excited if he has severe sleep disturbances, nightmares are concerned, etc.

- diuretics (Diacarb, Ariphon). This group of drugs is designed to remove excess fluid from the body, as well as for the prevention of the formation of brain edema;

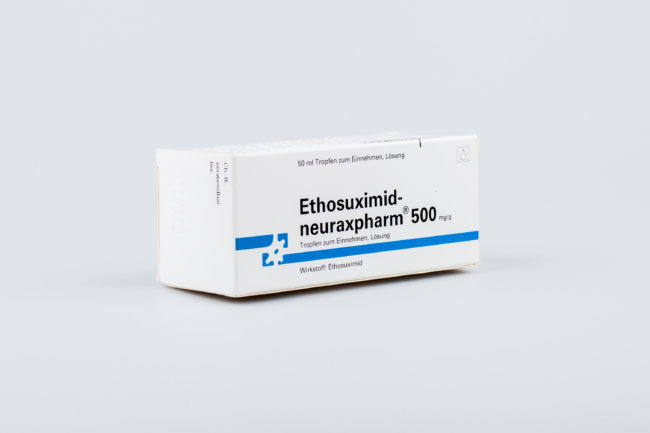
- anticonvulsants (ethosuximide, trimetadion). Drugs of this group are usually prescribed to patients with a severe degree of concussion. With such injury, convulsions can often occur;
- anti -warrior (cerucal, motilium). If cramps usually occur with severe concussion of the brain, then vomiting is the most common symptom even with a light concussion in both adults and in children;
- nootropic preparations (glycine, piracetam). The drugs of this group are designed to improve blood circulation in brain tissue, to improve metabolic processes in the brain. They are usually prescribed to patients with medium or severe degree of concussion;

- vasotropic preparations (Actovegin) are usually always prescribed to patients with a concussion taking nootropic drugs. Vasotropes need treatment of the problems of the vascular system. After concussion, the walls of some vessels can thicken or thin out, blood clots, etc. can form.
The decision to take a particular drug in a hospital is taken by the attending physician on the basis of the degree of concussion, examinations. It may be that the tablets with concussion are not needed at all. Additionally, the patient may be prescribed vitamin complexes that will help to speed up the recovery process. If the patient does not have complications, then the approximate time of stay with a concussion in the hospital in the hospital is one week, after which the patient is prescribed home, a number of drugs are prescribed, the regimen is prescribed. After hospitalization with a concussion of the brain, a second examination after a while by a neurologist, therapist is required.
The consequences of a concussion
A concussion of the brain even in a slight degree can have a number of consequences for humans. The most common of them are:
- headache within 1-2 weeks after a concussion;
- bouts of light dizziness;
- difficulties with concentration of attention, forgetfulness;
- sleep disorders.
If these symptoms do not pass after 2-4 weeks after a concussion, then be sure to consult a doctor for a second examination, excluding possible complications.
Complications of the concussion of the brain
The brain is not studied completely. It is for this reason that even the lightest concussion can “remind” of itself with rather dangerous complications after a while. We list some of them:
- inexplicable outbreaks of aggression and nervous excitability;
- inadequate reaction to alcohol;
- violation of coordination, shakiness of the gait;
- memory problems;
- fatigue;
- sweating;
- tides;
- sharp changes in blood pressure;
- convulsive seizures;
- depression, neurosis, phobia.
Some of the complications listed above are treated, while others can be irreversible.
If after a head hit, falling from a height, a bruise of the head, some symptoms appeared, then in no case do not ignore such “bells” of your body. It is especially careful about such conditions in children. Take care of yourself and your loved ones!








Comments
a couple of years ago, there was no side of metrogils from the same problem, there were no side effects ...
I’m not a fan of peeling at all, it saves from acne of metrogil, it also smoothes it ...
Great article! ...
I take the second course of the Capsules Climafite 911. The tides went very quickly. It became calmer, irritability went away and I sleep well ...
i also noticed - it is worth nervous, everything immediately affects the face. Therefore, I try to avoid conflicts and unpleasant people. Of the creams, I like Miaflow from wrinkles - smoothes not only small wrinkles ...