The condition when there is no strength and it would seem that it is not happy, today is familiar to almost every modern person. However, do not depress, because psychologists know how to deal with such a syndrome.
Content
The scale of such an emotional problem of modern society today is quite widespread among the adult population. And not surprising, because the template signs of burnout can be found in many others or yourself. The modern pace of life and the age of exploitation of everything and all inevitably leads to the rapid depletion of the body physically and psychologically.
If you notice that your activity at work and in public life has decreased significantly, then you should understand the causes of this state. The way out of this position depends on the level of stress that suppresses you and their number. You should also pay attention to the prevention of emotional burnout and those who feel positively inclined and continues to live with enviable activity so as not to lose joy in life.
The concept of emotional burnout syndrome
The very definition of psychological “burnout” (emotional burnout) was introduced by the American psychotherapist G. Freidenberg recently (1974). Such a syndrome in psychology is usually determined as a manifestation of prolonged depression and stress caused by overstrain or as a period of professional crisis. Any negative emotions should receive their expression and discharge, and if this does not happen, then personal emotions and energy of a person are exhausted.
Later, professors of the University of California Psychology have developed a scientific method for studying this problem, which involves a three -level group:
- Psychological exhaustion. Sensual oversaturation, lowering positive reactions to what is happening or complete indifference.
- Personality deformation. Deterioration of relations with others in society, a decrease in independence and independence, a manifestation of negative and cynical emotions to people.
- Reducing personal achievements. Negative self -esteem, restriction of opportunities, success, achievements and duties.
The reasons for emotional burnout
Modern psychology allows us to distinguish several basic stressogenes, which are saturated with our daily life and which lead to the occurrence of the syndrome:
- The need for constant intensive communication with society. Often arising problems and workdays make us face daily with many people, different in emotional state. If you are distinguished by modesty and isolation, then excessive concentration on your own and other people's problems will lead to stress and emotional discomfort.
- The need to work in conditions of increased efficiency. Every day, it requires us with composure, punctuality, self -organization, politeness and constant self -control. The publicity and excessive openness of our life makes us and others tightly control ourselves, which leads to internal instability and emotional irritation.
- Constant tension of the surrounding atmosphere. The accelerated rhythm of modernity and control of actions at work, as well as excessive workload and a catastrophic lack of free time for relaxation deplete our body. Stress is a natural consequence of overstated requirements and lack of external and personal energy resources.
Diagnosis of emotional burnout
In order to adequately assess your psychological state of health, all characteristic symptoms and signs of exhaustion are customary as follows:
- psychological;
- social behavior;
- physiological.
Physical symptoms of emotional burnout
The physiological aspects of burnout should be attributed:
- insomnia or violation of the regime of the day, a complete absence of sleep until early morning or sharp falling asleep, the inability to fall asleep in the middle of the night, severe awakening;
- violation of breathing and shortness of breath at any load;
- a reduced reaction to environmental changes, the complete absence of joy and curiosity or a sense of fear in case of danger;
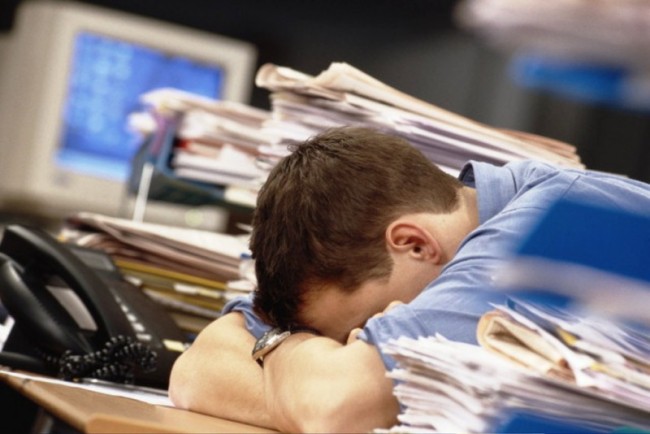
- constant physical fatigue, when a feeling of powerlessness does not pass even in the morning after a normal full sleep;
- constant desire to sleep, drowsiness, inhibition;
- constant headaches for no reason;
- a sharp change in weight indicators (decrease, increase);
- decrease in vision, smell, touch, hearing, loss of tactile sensations;
- chronic violations of the digestive organs and metabolic processes (constipation, diarrhea);
- a chronic sense of weakness, a decrease in energy reserves, a decrease in immunity, biochemical indicators in the blood and hormonal background;
- a sense of physical and psychological exhaustion.
Psychological signs of emotional burnout
The psychological aspects of burnout is customary to attribute:
- unreasonable nervous breakdowns, isolation, outbreaks of aggression and anger, detachment from others;
- negative attitude for the future and professional growth;
- increasing irritability, aggression and violent response to the events;
- constant excessive experience and a feeling of causeless anxiety, shame, guilt, resentment, shyness and suspicion;
- a sharp decrease in self -esteem and dissatisfaction with oneself;
- stress, depression, passivity, boredom, apathy, decrease in emotional reactions, a feeling of depression;
- chronic and inexplicable feeling of fear and a foreboding of a negative outcome and failure;
- excessive sense of anxiety and irregular position and situations.
Social aspects of emotional burnout syndrome
Social and behavioral burnout reactions include:
- alcohol abuse and cigarettes, overeating or complete absence of appetite, concentration, increase and appearance of harmful addictions and habits;
- change in the regime of day and sleep;
- inadequate criticism of others, alienated from loved ones;
- the impossibility of performing the main tasks due to the fixation on minor problems, a waste of useful time and energy on non-primary affairs;
- delayed plans the next day and failure to fulfill them as a result;
- a sense of noble work and catastrophic lack of energy resources;
- a sense of own uselessness, a decrease in interest and stimulus, indifference and indifference to the result;
- increased irritability, unreasonable anger and aggression, resentment, hysteria.
The levels of emotional burnout
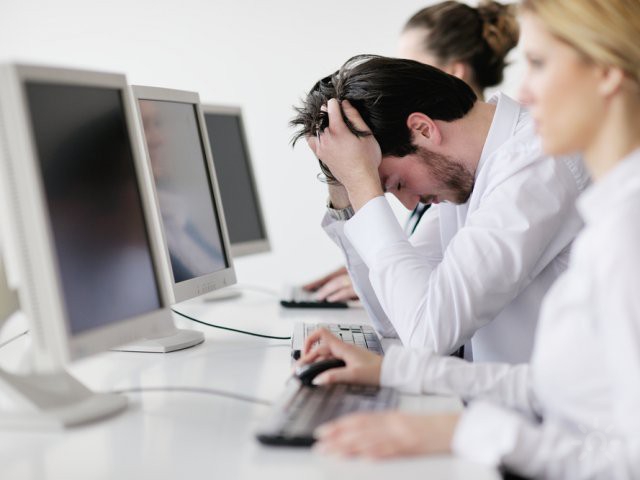
Psychological exhaustion or burnout can manifest itself unnoticed, and a person is practically not able to independently determine the beginning of emotional burnout syndrome. Diagnosis of the level of emotional burnout is often carried out by psychologists in the form of testing and allows you to detect symptoms of the syndrome as early as possible for its effective treatment.
The first stage of emotional burnout
At the first stage, emotions simply muffle, which manifests itself in mild indifference and insensitivity to what is happening and surrounding people. Also, increased dissatisfaction with oneself, life and sharp outbursts of response in relations in society are also manifested. At the physical level, a person often experiences unreasonable headaches, spasms in the back and seizures of the limbs, he is concerned about insomnia and frequent colds.
The second stage of emotional burnout
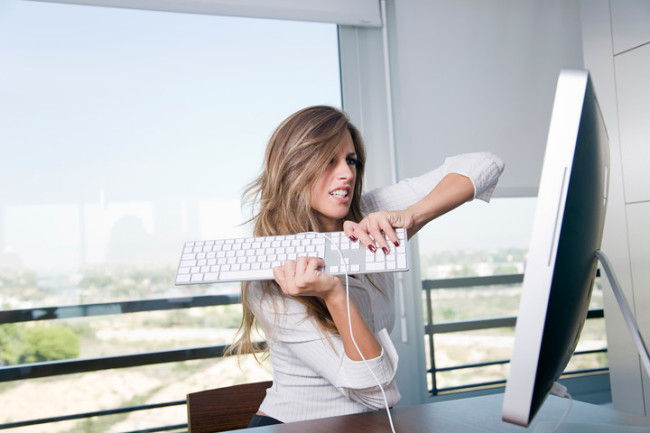
At the next stage, the syndrome of emotional burnout begins to appear more noticeably from the emotional side. Just as a mirror display, you begin to reflect your discontent and internal discomfort in the external manifestations of irritation, malice and aggression in relations with people with whom it is necessary to communicate throughout the day. In order to avoid a sharp unjustified aggression, a person can move away from others, close in himself and perform a minimum of the necessary work and not show activity in order to contact people in society as little as possible.
The third stage of emotional burnout
Irritation cannot last forever, so the third stage of burnout occurs - emotional and physical exhaustion. A person no longer has the strength to work, nor to fulfill his daily duties, or to rest and communication with loved ones. This stage is characterized by manifestations of sharp bitterness, grossness, rudeness, isolation and complete detachment from society, sometimes the fear of communication and inexplicable excitement when leaving the usual comfort zone is manifested, as well as the body is subject to serious diseases (dermatitis, asthma, ulcer, hypertension, cancer).
Emotional professional burnout
Psychologists have identified several professions that fall into the first group of risk zone for burnout syndrome:
- Medical workers.
- Social workers.
- Teachers.
- Senior managers and managers.
- Employees of law enforcement agencies.
- Management workers.
- Professions related to constant travel departments.
- Service workers in constant contact with people.
- Working in harmful conditions (noise, vibration, contaminated air).
- Working on a shift schedule, without a specific recreation and nutrition mode.
In addition to professional affiliation of psychological burnout, any person can be subjected to, at whose work organizational changes and conflicts are constantly taking place. Much depends on personal qualities, for example, extroverts are subjected to burnout less often introverts. People with high ideals and high personal requirements, as well as those who are not used to distinguishing work and personal lives, fall into the risk zone.
People subject to stress, prone to empathy, dreams, psychologically unstable and idealizing events and society are more susceptible to such burnout. In addition, each person has periods of professional crisis (usually experience from 10 to 15 years of work), during which a person either develops further, or work ceases to interest him and delight him. The impossibility of career growth, the lack of stimulus and constant vocational training is one of the most important factors that leads to the psychological apathy of a person.
Prevention of emotional burnout
The lower risk of psychological burnout people with such qualities are subject to:
- adequate self -esteem of abilities and confidence in personal capabilities;
- good health;
- regular care for physical condition (healthy lifestyle, playing sports).
Also, people with experience in the experience of positive overcoming problems and capable of quick adaptations to changes in the surrounding conditions are also less affected. Such people are distinguished by independence, a positive mood, the desire to communicate and make acquaintances, an indefatigable desire to learn and travel. An important characteristic of people's unperemitted stress is an optimistic mood in relation to themselves, others and what is happening.
So, the prevention of emotional burnout syndrome is the following means:
- Sport. Physical activity is not only a good prevention of diseases and excess weight, but also a panacea from all psychological injuries. Another thing is that someone is suitable for yoga and meditation, to another-hardening, morning jogging or charging in the morning, and for others, group classes in the gym or in dance sections are ideal.
- Rest. The efficiency of work directly depends on full relaxation. On vacation, just like a job, you need to spend some time to return to duties with a new portion of energy. It can be a change of scenery in connection with the trip, and new positive impressions of meeting with friends, and even getting a portion of adrenaline for extreme lovers.
- Mode. An ordered and planned day will help to concentrate on work in a timely manner and train the body in a timely manner to the prescribed rest.
- Psychological defense. The ability to put an imaginary barrier among themselves and an unpleasant person will allow you to control your emotions and not respond to possible emotional provocations of others, which will preserve your nerve cells and save from unnecessary stress.
- Harmony. Keep your inner calm and mental balance, do not mix work and personal life, but conduct conversations on common abstract topics. Do not waste personal energy resources to discuss your personal life and problems, both your own and your colleagues. Keep personal problems only for very close people and do not waste explanations or empathy with acquaintances and employees.
Video about the emotional outcast of the personality
Available video about psychological burnout syndrome will help in the fight against the problem:















Comments
a couple of years ago, there was no side of metrogils from the same problem, there were no side effects ...
I’m not a fan of peeling at all, it saves from acne of metrogil, it also smoothes it ...
Great article! ...
I take the second course of the Capsules Climafite 911. The tides went very quickly. It became calmer, irritability went away and I sleep well ...
i also noticed - it is worth nervous, everything immediately affects the face. Therefore, I try to avoid conflicts and unpleasant people. Of the creams, I like Miaflow from wrinkles - smoothes not only small wrinkles ...